8 precursors essential for biosynthesis of alkaloids
by egpat 10-10-2017
Amino acids act as important bio precursors for the biosynthesis many alkaloids. They are modified in several ways producing various intermediate precursors which are finally converted into the alkaloids in the plants. Here we will discuss few of the important amino acids and other mediator acting as precursors for biogenesis of alkaloids.
First let’s list out the amino acids involved in the biosynthesis of alkaloids.
- Tyrosine
- Tryptophan
- Ornithine
- Lysine
- Histidine
- Phenyl alanine
Apart from the above amino acids, few of the other substances also play role as precursors. They include
- Nicotinic acid
- Anthanilic acid
How they are involved?
OK, amino acids act as precursors but how they are involved in the synthesis of alkaloids?
Amino acids can be incorporated in alkaloids two ways.
- Entire carbon skeleton except carboxylic acid
- Only nitrogen in amino acid
Those amino acids which incorporate the entire carbon skeleton except carboxylic acid are known as true alkaloids. Various examples included in this category are
- Indole alkaloids
- Quinoline alkaloids
- Isoquinoline alkaloids
- Tropane alkaloids
- Imidazole alkaloids
On the other hand, those alkaloids which incorporate only nitrogen atom from the amino acid and remaining carbon skeleton is derived from non-amino acid source are called as pseudo alkaloids.
Examples include
- Purine alkaloids
- Terpenoid alkaloids
- Steroidal alkaloids
Another category of alkaloids are also present which include the entire carbon skeleton except nitrogen from amino acid. These are called as proto alkaloids as then nitrogen in these alkaloids is outside of the ring system
So, let’s start out discussion with each amino acid and how they derive various alkaloids.
1. Tyrosine
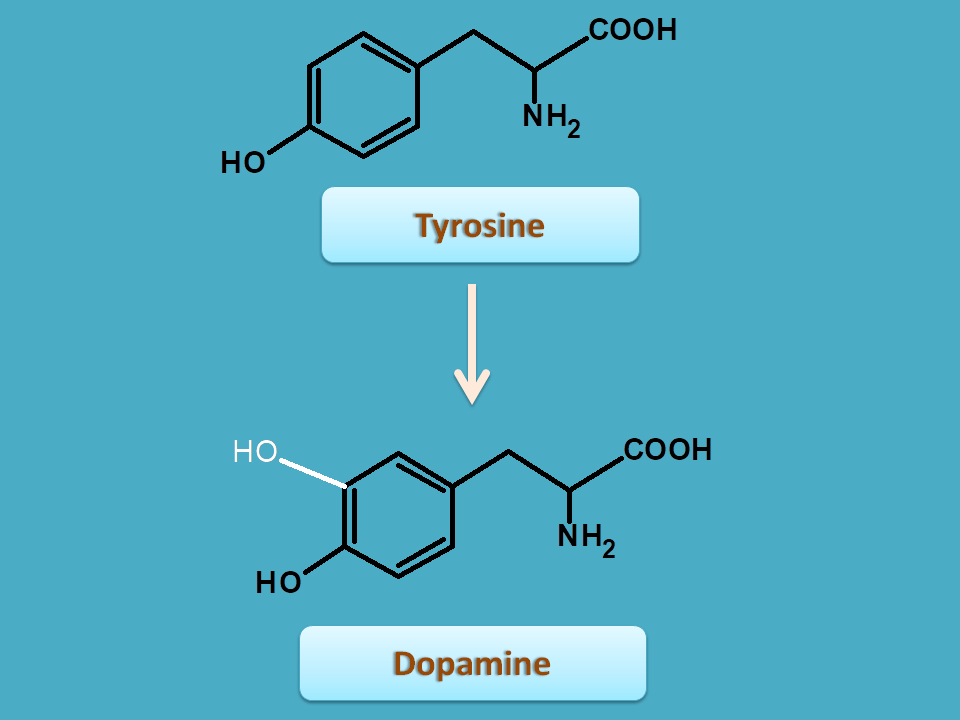
Tyrosine is an amino acid with phenyl ring having hydroxyl group at para position . It can be converted into various other intermediates which are involved in the biosynthesis of isoquinoline alkaloids. One of such important intermediate is dopamine.
Within the plant tyrosine is converted in to dopamine. This conversion uses the entire skelton of tyrosine with adding hydroxyl group at 3rd position. The groups are carbons which are newly added are shown by white color.
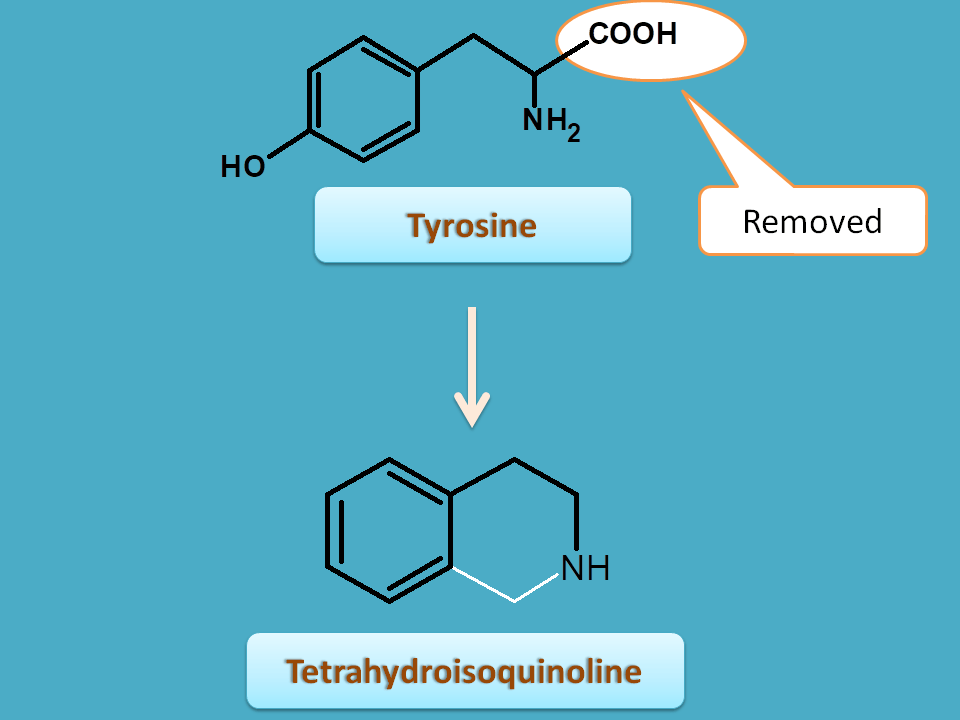
Similarly another intermediate is tetrahysroisoquinoline. Here carboxylic acid is removed from tyrosine and the remaining skeleton is incorporate into the cyclic structure.
Tyrosine can also be incorporated as benzyl tetrahydroisoquinoline with addition of benzyl group by an aromatic aldehyde.
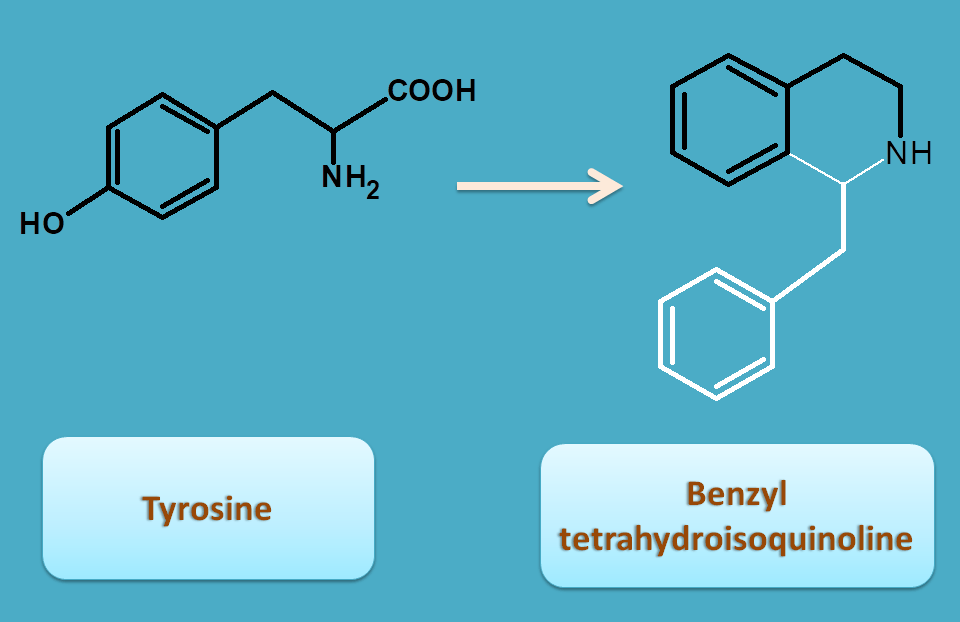
Here again you can observe that those bonds shown by black color are derived from tyrosine.
By all these discussion, we can conlude that tyrosine acts as precursor for isoquinoline alkaloids.
Isoquinoline alkaloids are derived from tyrosine.
❞Again isoquinoline alkaloids are distributed in various plants with little modification and hence classified into the following types.
- Bis benzyl tetrahydroisoquinoline
- Modified benzyl tetrahydroisoquinoline
- Phenethylsioquinoline alkaloids
- Terpenoid tetrahydroisoquinoline
Bis benzyl tetrahydroisoquinoline
Here two molecules of benzyl tetrahydroisoquinoline are fused two produce bis benzyl tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloids.
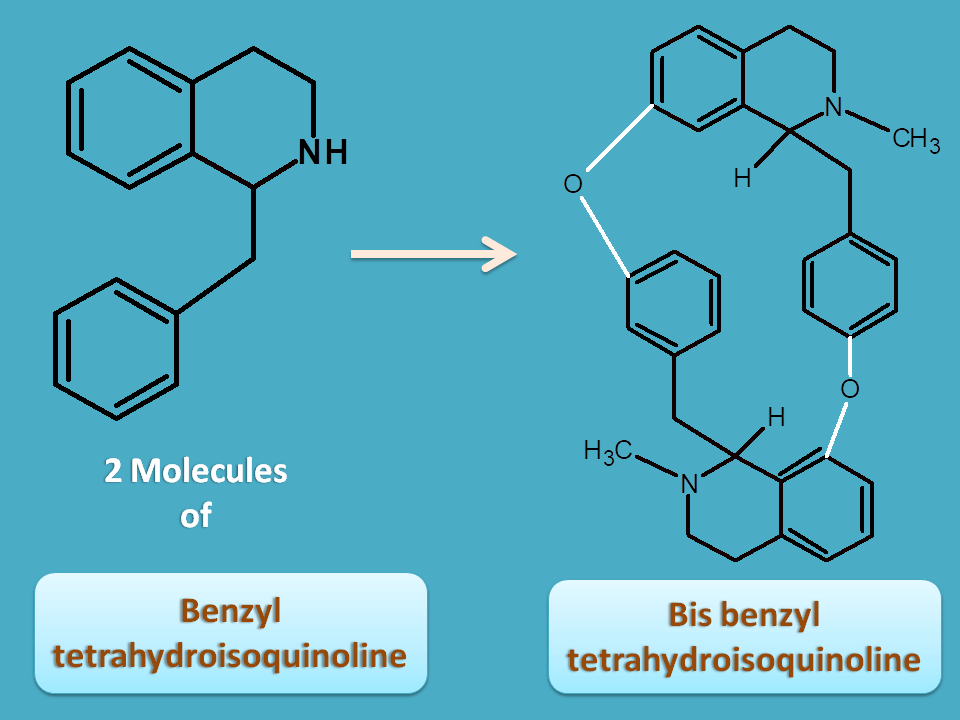
One of the example of alkaloid in this category is d-Tubocurarine. It is obtained from dried extract of stems and leaves of Chondrodendron tomentosum belonging to the family of menispermaceae.
It acts as non-depolarising neuromuscular blocker that blocks nicotinic acetylcholine receptors at neuromuscular junction and thereby produced skeletal muscle relaxation. It olden days it is used as arrow poison as it relaxes skeletal muscles of animal preventing their escape during hunting.
Modified benzyl tetrahydroisoquinoline
These alkaloids are derived from benzyl tetrahydroisoquinoline with a little modification of structure by opening of ring followed by rotation and ring closure yields clinically important opium alkaloids
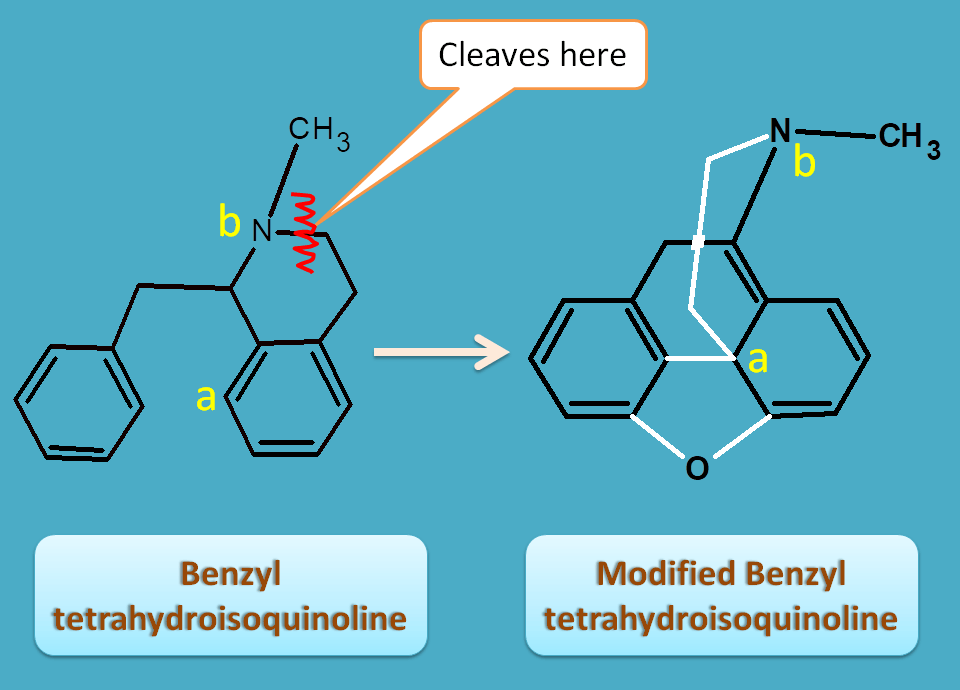
The ring is cleaved at tetrahydroisoquinoline moiety and it is closed at atoms labeled by “a”and “b”by an ethyl bridge.
Opium alkaloids are obtained from dried latex of unripe capsules of Papaver somniferum belonging to the family of papaveraceae.
Various important opium alkaloids naturally present in these plants are
- Morphine
- Codeine
- Thebaine
Thebaine acts as important source for semi-synthesis of new opioids.
Opioids are used as analgesics in chronic and severe pain conditions and they act by inhibition of nociceptive neurons by openining of potassium channels.
Other type of alkaloid like papvarine is also present in these plants which act as smooth muscle relaxant.
Phenethylsioquinoline alkaloids
These alklaoids are obtained from fusion of dopamine with phenyl alanine forming a new 8 numberd ring system “tropolone” ring.
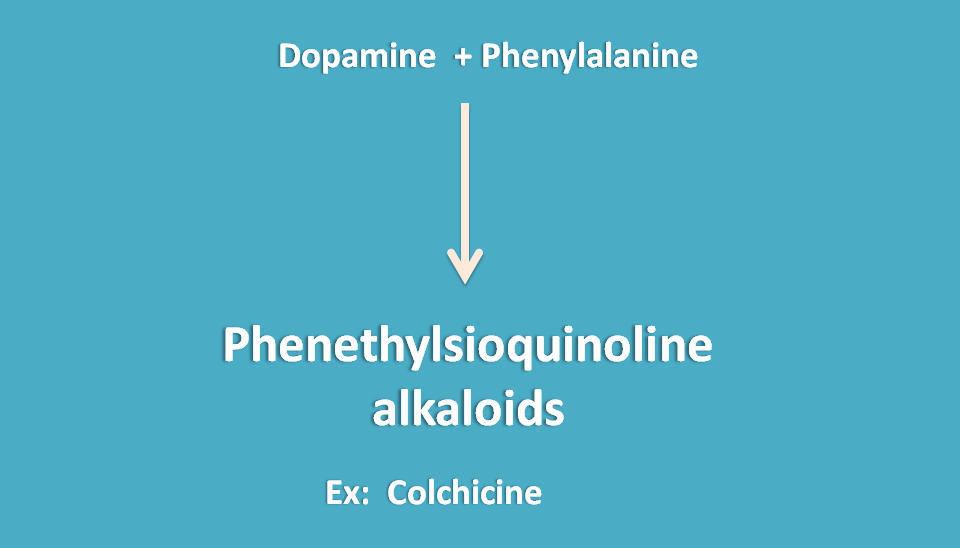
Colchicum is the alkaloid belongs to this category that is obtained from seed and corm of Colchicum autumnale belonging to the family of liliaceae.
This plant mainly contains
- Colchicine
- Demecolcine
Colchicine inhibits microtubule formation and decreases uric acid levels. Hence it is used as anti-gout agent.
Terpenoid tetrahydroisoquinoline
Here two molecules of dopamine are incorporates along with a terpenoid like secologanin to produce terpenoid tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloids.
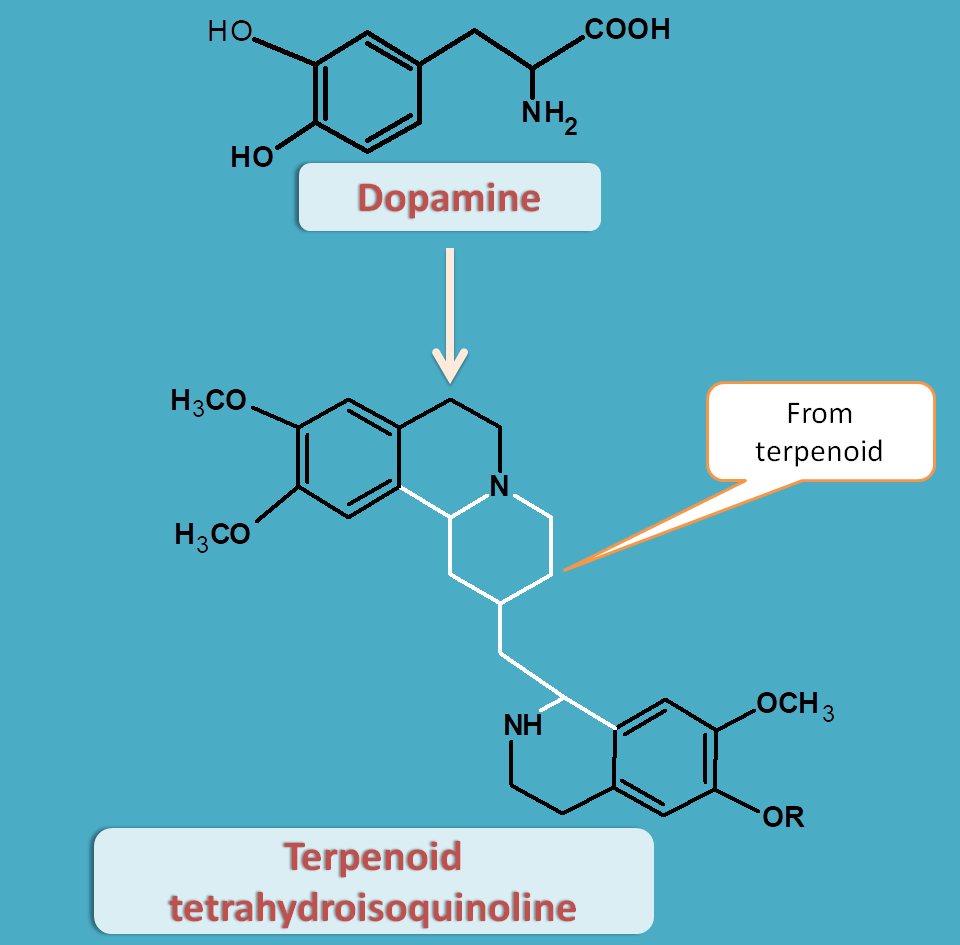
Ipecac obtained from Cephaelis species like Cephaelis ipecacuanha or Cephaelis
acuminata belong to this category.
The main chemical components in these alkaloids are
- Emetine
- Cephaline
- Psychotrine
- O-methyl psychotrine
These alkaloids are bitter substances and act as emetics.
2. Tryptophan
Tryptophan is converted into tryptamine by decarboxylation. 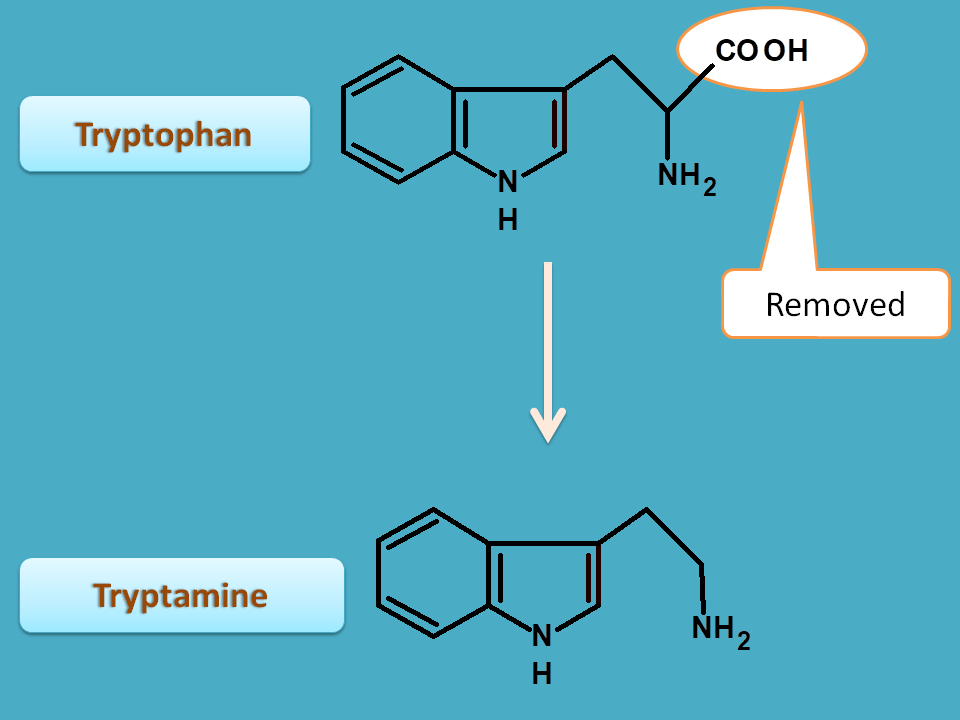
Trypamine acts as precursor for two types of alkaloids
- Quinoline alkaloids
- Indole alkaloids
Quinoline alkaloids
Tryptamine undergoes a ring opening followed by rotation and ring closure steps to produce quinoline nucleus. You can observe the atoms indicated by letters like a,b and c are incorporated in quinoline nucleus.
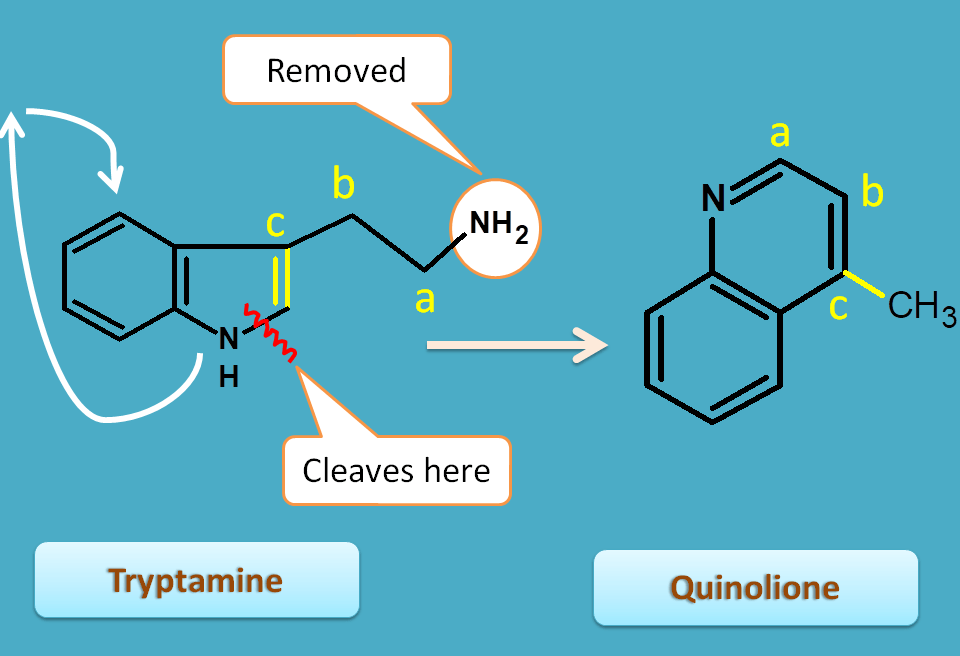
Cinchona is a quinoline alkaloid obtained from Dried root or stem bark of Cinchona species like Cinchona calisaya, Cinchona officinalis belonging to the family of rubiaceae.
Four important alkaloids found in these plants are
- Quinine
- Quinidine
- Cinchonine
- Cinchonidine
Quinine is used as antimalarial agent whereas quininidine is a class Ia antiarrhythmic agent. The later blocks voltage gated sodium channels hence decreases ventricular arrhythmias.
Indole alkaloids
Tryptophan is also serves as precursor for indole alkaloids.
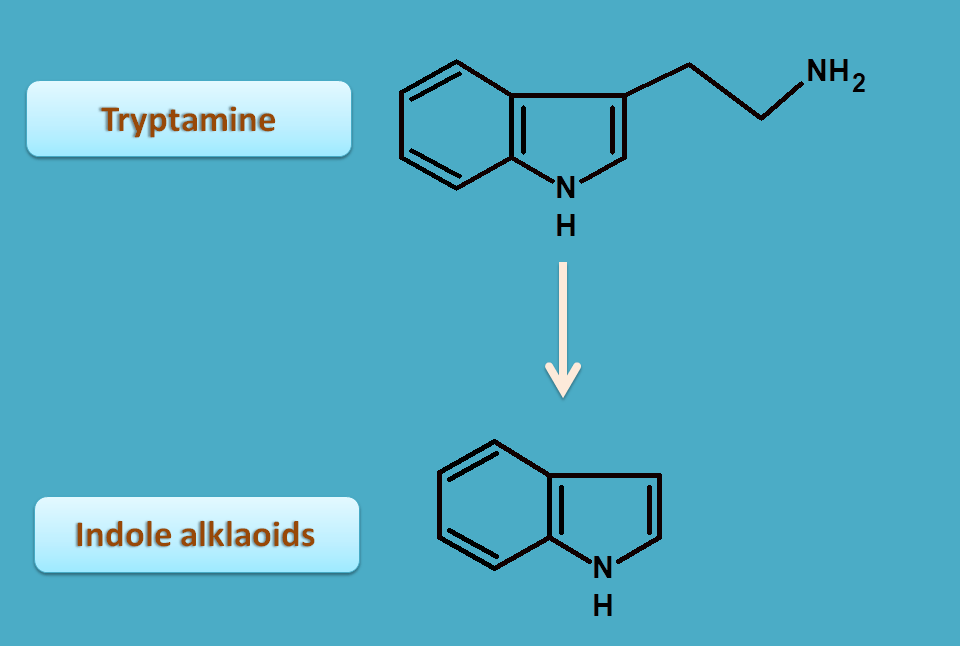
Indole alkaloids are furter classified into
- Terpenoid indole alkaloids
- Rauwolfia
- Vinca
- Nuxvomica
- Pyrroloindole alkaloids
- Physostigma
- Ergot alkaloids
- Ergot
Terpenoid indole alkaloids
Terpenoid indole alkaloids are derived from tryptamine combined with a terpenoid like secologanin.
a. Rauwolfia
Rauwolfia is obtained from dried rhizome and roots of Rauwolfia serpentine commonly called as snake root belonging to the family of apocynaceae.
The main chemical constitutes in the plant are
- Resperpine
- Rescinnamine
- Ajmalicine
Reserpine is adrenergic storage inhibitor previously used as antihypertensive but nowadays less preferred due to its side effect like psychosis and depression.
b.Vinca
Vinca alkaloids are one of the important natural anticancer agents that made a big hit in the treatment of luekemias.
Vinca is obtained from entire plant of Catharanthus roseus belonging to the family of apocynaceae. It is also called as Madagascar periwinkle.
The two main chemical consitutents present in vinca are
- Vincristine
- Vinblastine
It also contains small amount of ajmlicine.
Vindesine and vinorelbine are semi-sythetic derivatives of vinka alklaoids.
c.Nuxvomica
It is obtained from seeds of Strychnos nux-vomica.
The main alkaloids prenet in the plant are
- Strychinine
- Brucine
Both of these are bitter substances and used as emetics. Strychinine is a CNS stimulant that produces convulsions.
Pyrroloindole alkaloids
Physostigma is a pyrroloindole alkaloid biosynthesized from tryptamine by ring closure.
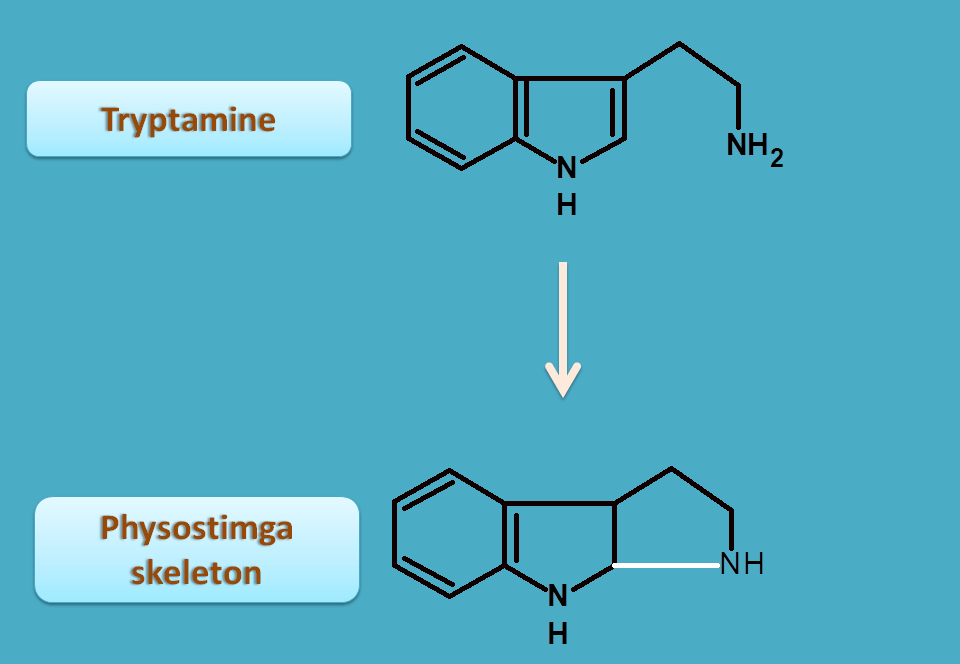
It is commonly called as calabar beans obtained from seeds of Physostigma venenosum belonging to the family of Loganiaceae
It mainly contains physostigmine as principle alkaloid.
Phsostigmine also called as eserine acts as medium acting acetylcholine esterase inhibitor thereby increases cholinergic transmission at synaptic cleft. It is indicated for the treatment of glaucoma as eye drops.
Ergot alkaloids
Ergot alkaloids are again derived from tryptamine by several reaction with lysergic acid as an intermediate.
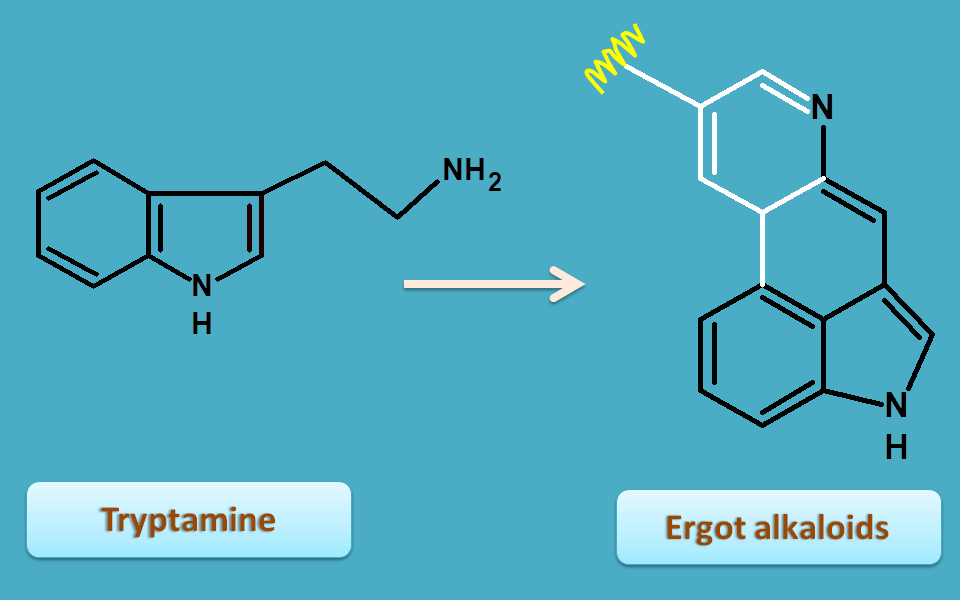
Ergot is obtained from fungal sclerotium of Claviceps purpurea belonging to the family of clavicipitacea.
Ergot is also called as St. antony’s fire due to ergotism, the symptoms collectively it produce.
This plant contains various alkaloids derived through lysergic acid are mainly divided into four groups
- Water soluble
- Ergotamine
- Water insoluble
- Erometrine
- Ergotoxine
- Ergoxine
Ergotamine is used in the treatment of migraine whereas ergometrine is used in postpartum hemorrhage.
3. Ornithine
Ornithine is an aliphatic amino acid which undergoes cyclization with removal of carboxylic acid produces pyrrolidine nucleus.
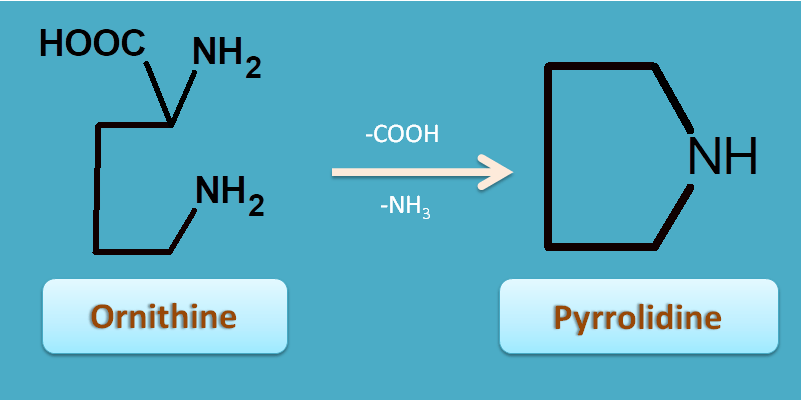
This ring can be further substituted to form tropane nucleus.
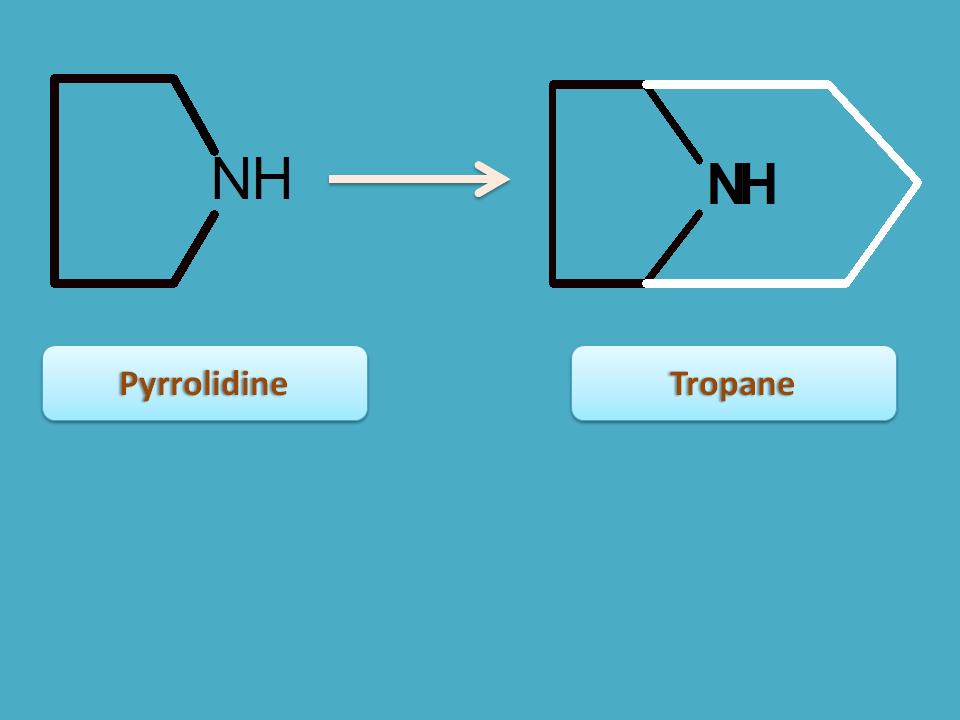
Various types of alkaloids having tropane nucleus are
- Belladona
- Datura
- Hyoscyamus
All these plants have the following chemical constituents with little difference in their percentages.
- (-)-Hyoscyamine
- Atropine
Atropine is a recemic mixture of hyoscyamine and acts as anticholinergic by blocking muscarinic acetylcholine receptors.
Atropine is an ester of tropanol and tropic acid where tropic acid is biogenetically supplied from phenyl alanine.
Another type of plant also contains tropane nucleus with little modification is coca alkaloids.
They contain cocaine one of the drug that shows high addiction and used as local anesthetic.
4. Lysine
Just like ornithine, lysine is an aliphatic amino acid with 6 carbons that undergoes cyclization by removal of carboxylic acid and therefore forms 6 membered piperidine nucleus.
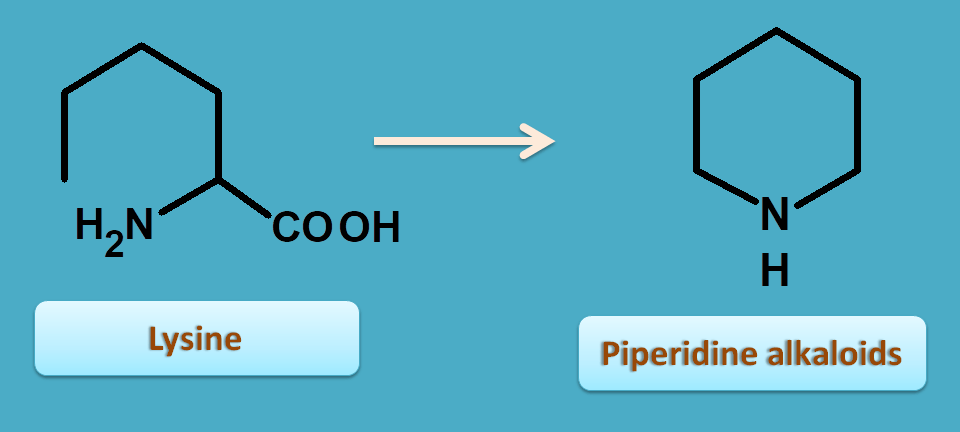
Two important alkaloids belonging to this category are
- Lobelia
- Areca
Lobelia
Lobelia is obtained from Dried leaves and tops of lobelia inflata
It mainly contains
- Lobeline
- Lobelanidine
These are used as respiratory stimulants.
Areca
Areca is obtained from dried ripe seed of Areca catechu belonging to the family of palmae.
It mainly contains
- Arecoline
- Arecaidine
These are again used as respiratory stimulants.
5. Histidine
It can be clearly identified that imidazole nucleus is obtained from histidine by removal both amine and carboxylic acid groups.
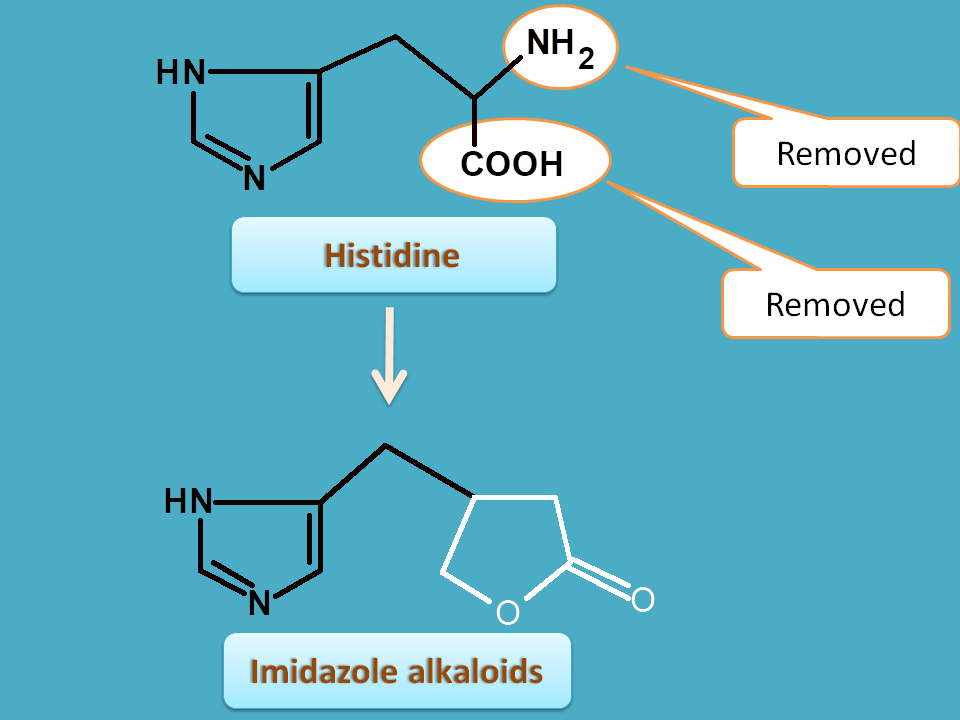
Pilocarpus obtained from dried leaves of pilocarpus jaborandi belonging to the family of rutaceae.
It mainly contains
- Pilocarpine
- Isopilocarpine
Pilocarpine is a muscarinic agonist used in the treatment of glaucoma.
6. Phenyl alanine
Phenyl alanine acts as precursor in many alkaloids for supplying C6-C2 chain as we discussed above. For example it is involved in biosynthesis of
- Tropane alkaloids
- Colchicum alkaloids
In few alkaloids like ephedra, it can act as main precursor supplying the main skeleton of the alkaloid.
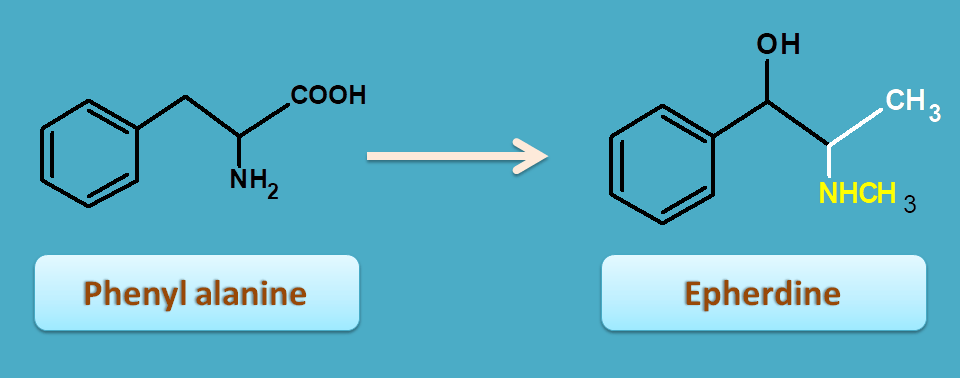
Ephedrine is a mixed acting sympathomimetic that acts both directly as well as indirectly on adrenergic receptors. It is used as nasal decongestant.
7. Anthranilic acid
Anthranilic acid is a ortho amino benzoic acid which is combined with other carbon skeleton to form a cyclic ring structure quinazoline.
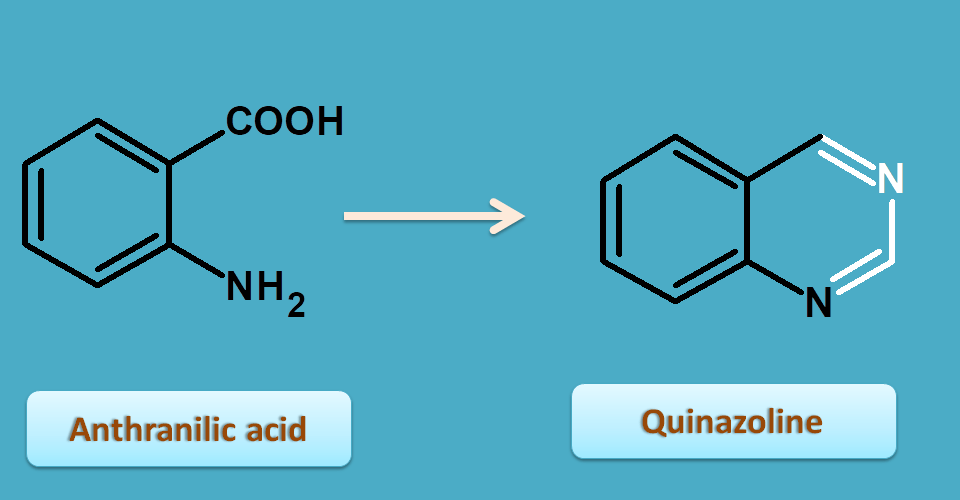
Vasaka is belongs to this class and is obtained from leaves of Adhatoda vasica belonging to the family of acanthaceae.
The principal alkaloids in this plant are
- Vasicine
- Vasicinone
These are used as expectorants,
8. Nicotinic acid
Nicotinic acid itself contains pyridine nucleus and acts as precursor for pyridine alkaloids.
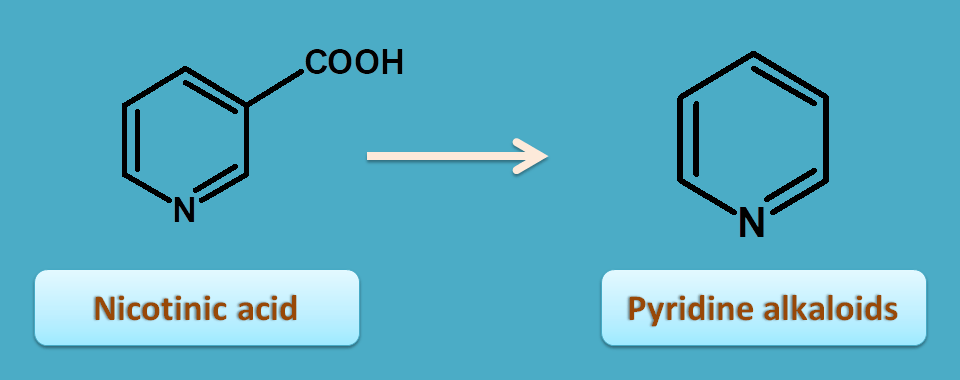
One of the pyridine alkaloid is tobacco obtained from Nicotiana tabacum belonging to the family of solanaceae.
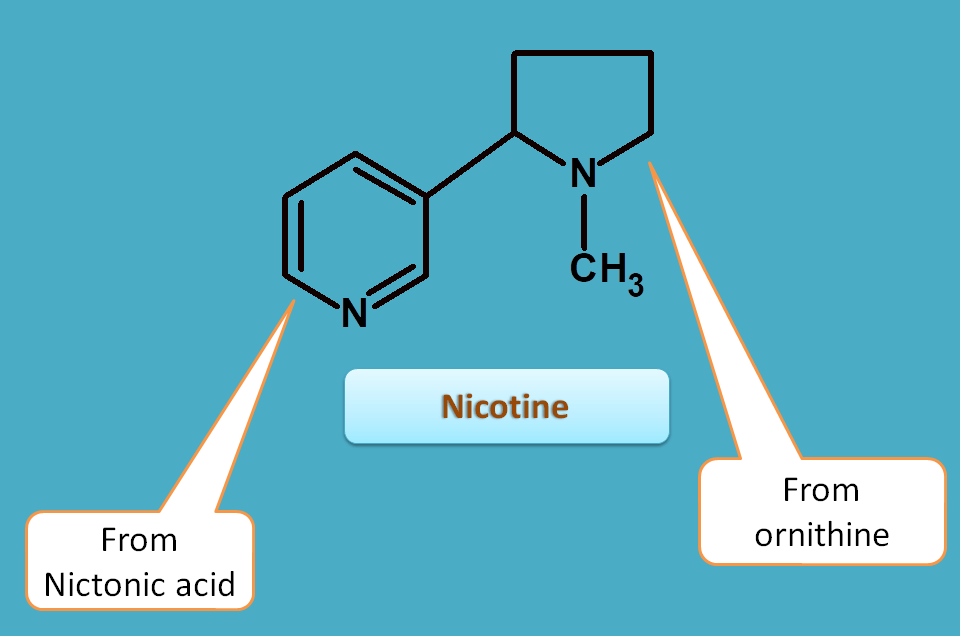
It mainly contains nicotine which has pyridine ring attached with pyrrolidine ring.
Nicotine is an agonist on nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and produces excitation of CNS, release of adrenaline, contraction of skeletal muscle.
So this is about the 8 types of precursors involved in biosynthesis of various alkaloids. They can be converted into important intermediates which may then directly involve in biosynthesis. Please don't forget to share this post, if you like it.