Electromagnetic spectrum - A collection of EMR
by egpat 05 Jun 2019
We are in a world equipped with electromagnetic spectrum consisting different types of electromagnetic radiation each related to our life at any one moment. For instance, we are all able to see and live because of visible radiation, we can’t imagine life without it. We use ultra-violet radiation for getting purification of water.
Each electromagnetic radiation can be characterized by its frequency or wavelength. Of course each EMR will have its own electronic energy specifically. The collection of all these different types of electromagnetic radiation is collectively known as electromagnetic spectrum.
EM spectrum
Even we can differentiate different types of electromagnetic radiation by their frequency or wave length, we can’t lay exact boundary between different types of radiation and often they overlap with each other.
Here we will go with discussion of how EM spectrum occupies significant role in our day to day life.
γ-radiation
This is the highest form of the electromagnetic radiation within the EM spectrum. These high energy beam are highly harmful and when they fall on the living system they can cause damage to nucleus in the cell. This may result in genetic mutations and subsequent unwanted reactions.
X-radiation
First we start with X-rays. These are highest energy electromagnetic radiation and when they fall on the matter they produce nuclear transitions. Since these are highly energetic radiation they can pass through our skin and muscles but not through the bones. Hence X-radiation can used for diagnostic purpose for detecting structural changes of bones and joints.

Is there any other role?
Defineitely, we have one more important application of x-radiation in analysis of compounds. X-ray fluorescence can be used for estimation of the compounds.
X-ray diffraction is another technique where X-radiation is allowed to fall on a target and diffraction pattern is studied to estimate the interatomic distances in the molecule. That’s why X-ray diffraction pattern sometimes considered as finger print spectra.
UV radiation
Next to X-radiation, UV radiation occupies its place within EM spectrum. It normally ranges from 10 nm to 400 nm. For practical purpose, this range can be further divided into two regions.
- Vacuum UV region
- UV region
Vacuum UV region is from 10 nm to 200 nm whereas normal UV region is from 200 nm to 400 nm.

Note: Normal UV region is sometimes considered from 180 nm to 360 nm. But for better classification, we can consider it from 200 to 400 nm.
Vacuum UV region is not suitable for analytical purpose and many of the solvent used in spectroscopy absorb radiation within this region.
Normal UV region is widely used for both qualitative and quantitative purpose and it is often combined with visible region to produce UV-visible spectroscopy.

UV radiation has a quite important in sterilization of industrial equipment. It is an ionizing radiation that can cause nuclear damage in the micro organisms hence used for sterilization. Another advantage of UV radiation compared with chemical sterilization is that it can be irradiated to the inner parts of equipment where chemicals can’t have full access for effective sterilization.
UV radiation can also be used for purification of water, generally reverse osmosis is combined with UV radiation to decrease the microbial load in the water.
Visible radiation
Nothing to say more about this as we read, see, walk, live only with the help of this radiation. Even colours of our life depend on visible radiation. This ranges from 400 nm to 800 nm.

As you know tungsten lamps, CFL lamps and LEDs all emit visible radiation bringing our daily activities smooth and colourful.
IR radiation
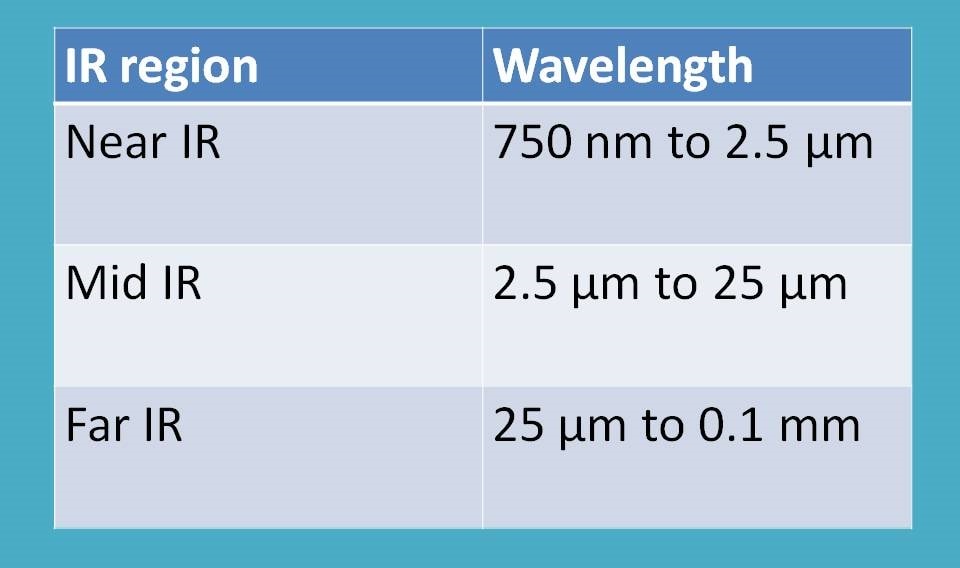
Interestingly, IR radiation ranges from 14000 cm-1 to 100 cm-1. This range can be further divided into three regions based on their interaction with matter.
- Near IR region
- Mid IR region
- Far IR region
As reflected in the name, near IR region is nearer to visible radiation. It ranges from 14000 cm-1 to 4000 cm-1. Mid IR region ranges from 4000 cm-1 to 400 cm-1 where as far IR region is from 400 cm-1 to 100 cm-1.
Among these, mid IR region is widely used for many of the analytical purpose such as identification of structure of new chemical compounds. It can also be used as finger print spectra to match with the standard IR plots and thereby identify the nature of the compound.
Microwave radiation
Microwaves are somewhat less energetic and they range from 0.1 mm to 1 mm. These radiation can be used in one of the technique called electron spin resonance (ESR) which is used to study the presence of unpaired electrons.

Again in our daily life we use microwave ovens for cooking and heating. Microwaves can also be used for drying of pharmaceutical ingredients.
Radiowaves
These are lowest energy radiation that fall at bottom of the electromagnetic spectra table. Their wavelength fall above 1 mm and they are not sufficient to produce any electronic transitions when interact with matter.

But they can change the spin of a nucleus hence used in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy.
Can you guess where we use them in ordinary life?
Yes, these are responsible for transmission of signals locally to short distances as observed in radio channels.