Digoxin is a cardiotonic but how it is indicated for atrial fibrillation?
by egpat Posted on 09-06-2017
Atrial fibrillation involves high rate of contraction of atria which are irregular and chaotic. These high rate of impulses in atria doesn't cause marked effect on function of the heart immediately but if untreated may be converted into more fatal ventricular arrhythmias.
The impulses which are generated in atria may be conducted into ventricles via AV node to initiate ventricular arrhythmias.
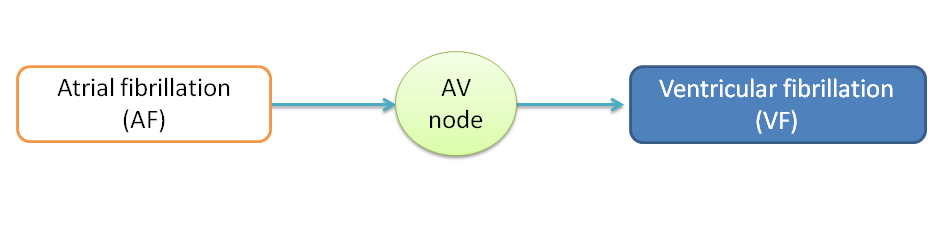
Hence to prevent further fatal arrhythmias, drugs which block AV conduction are used.
Digoxin is cardiotonic
Yes, digoxin is a cardiotonic i.e. it increases the tone of cardiac muscle which results in increased force of contraction. As it increases the force of contraction and thereby cardiac output, it can be used as an ionotropic agent in heart failure. On the other hand it has quite opposite role on rate of contraction of heart.

Digoxin increases vagal activity resulting in enhanced parasympathetic activity. This results in slowing of heart and decrease in calcium mediated AV conduction. As it decreases AV conduction, few number of impulses only reach to ventricles preventing ventricular fibrillation.

Hence digoxin has advantage in case of atrial fibrillation. Particularly it can be used in the treatment of heart failure associated with atrial fibrillation. At the same time digoxin should be carefully used as it can produce heat block due to slowing of AV conduction.