How quinidine increases the concentration of digoxin when given concomitantly?
by egpat Posted on 09-06-2017
Quinidine is a class I antiarrhythmic agent that shows pharmacokinetic interaction with digoxin. Normally pharmacokinetic interactions can take place at of the four important process such as absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion.
Now let’s check the possibility of interaction at above steps.
First at absorption. Both quinidine and digoxin neither interfere with any absorption process nor form any complex to interfere absorption.
Second at distribution. Quinidine as more lipophilic than digoxin it displaces the digoxin from protein binding sites. But this may cause a little change in the concentration of digoxin.
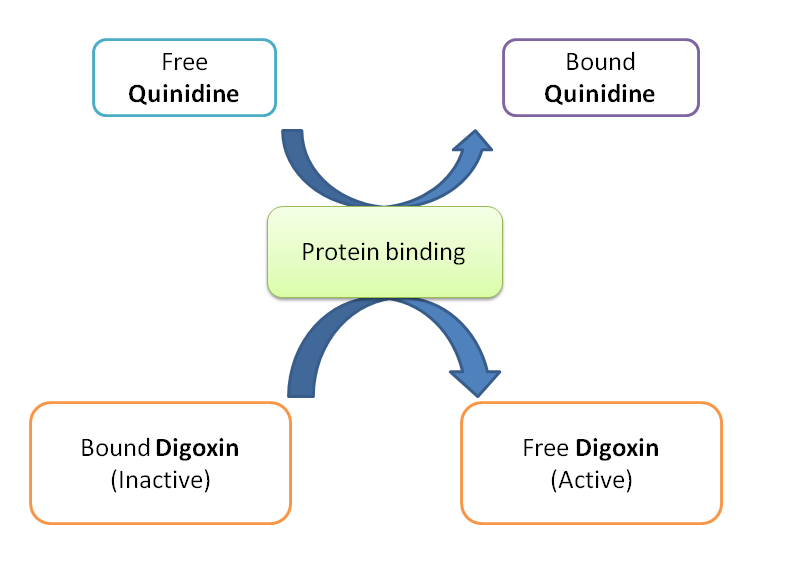
Third at metabolism. Most of drug interactions are possible at metabolism in which one of the drug acts as either enzyme inducer or enzyme inhibitor. Again here both quinidine and digoxin are neither enzyme inducers nor inhibitors.
Fourth at excretion.
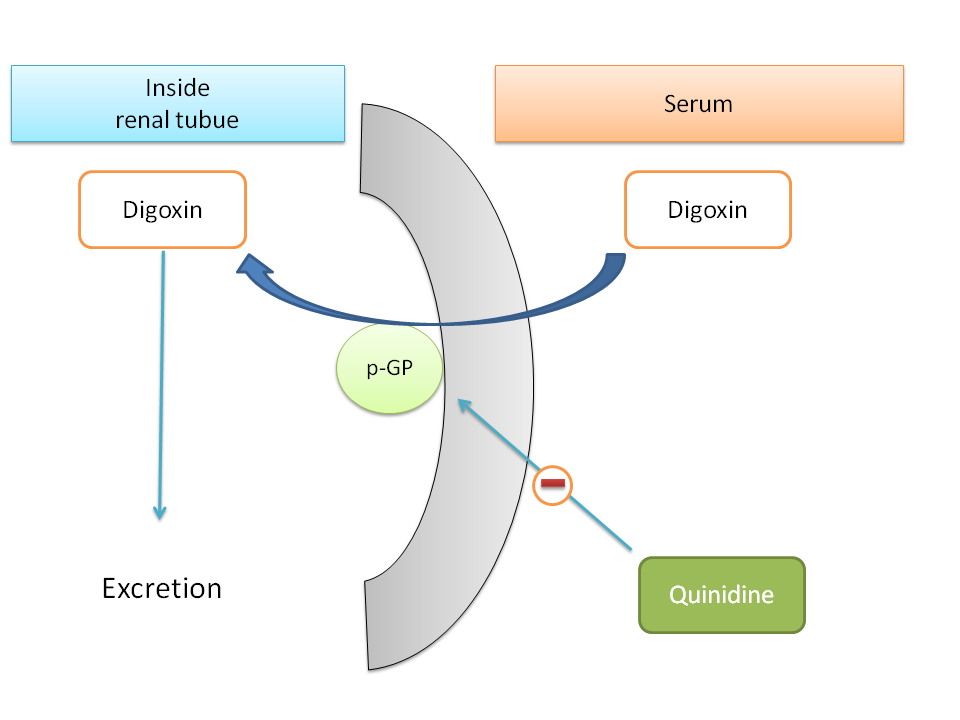
Quinidine inhibits p-glycoprotein pump present at renal tubules which is responsible for secretion of drugs like digoxin in to renal tubules leading to their excretion.
Quinidine, thereby inhibits the excretion of digoxin leading to its increased serum levels.
Other drugs that show similar interaction with digoxin include Calcium channel blocker like verapamil, Potassium channel blocker like amiodarone.
Here watch this video clearly explaining the interaction.