Is Levodopa not preferred for Parkinson disease in younger patients?
by egpat Posted on 25-07-2017
Parkinson disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder mainly due to loss of dopaminergic neurons in nigrostriatal pathway within the CNS. This results in motor disturbances like bradykinesia, muscle rigidity and resting tremor etc.
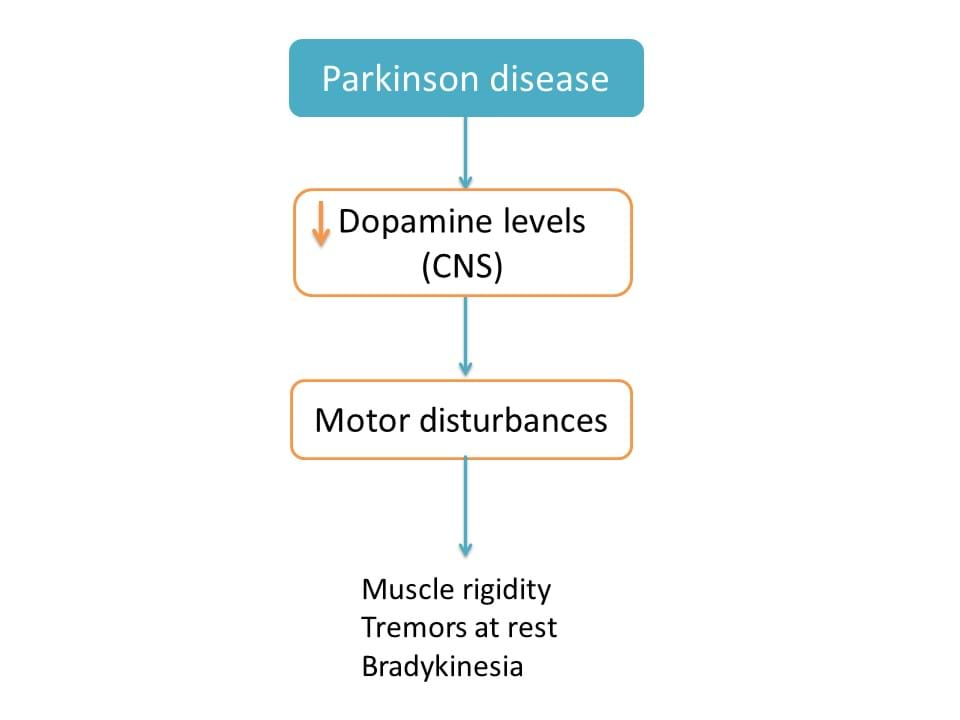
So, one of the main goal in Parkinson disease is to increase dopaminergic transmission within the CNS.
This can be accomplished by two category of drugs such as
- Dopamine precursors
- Dopamine agonists
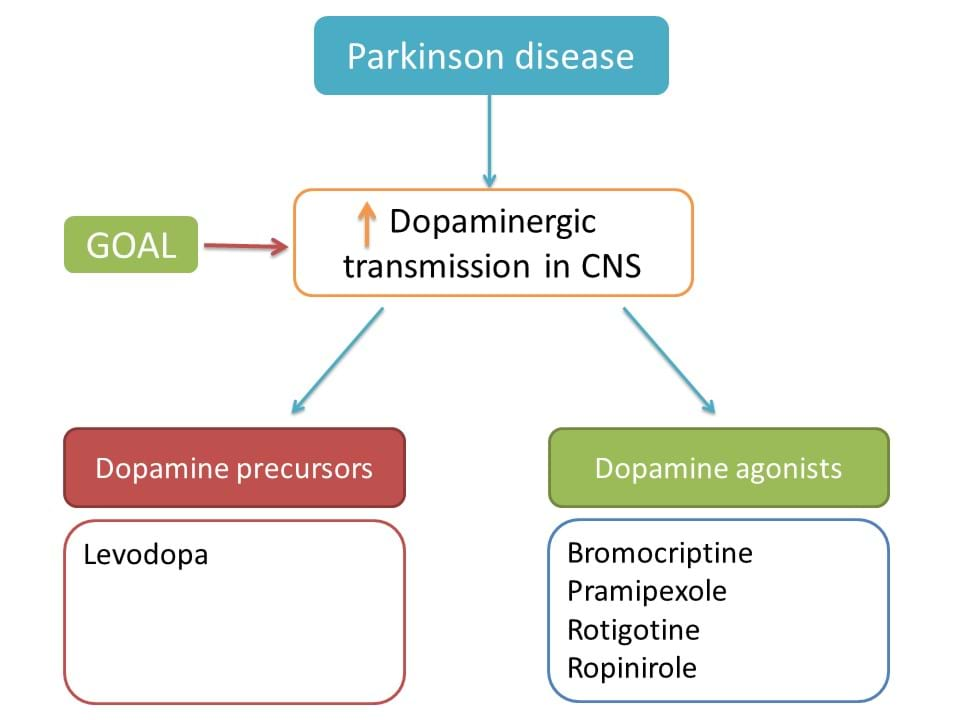
Other drug targets such as COMT inhibitors, MAO inhibitors , amantadine and anticholinergics act by other mechanisms and mainly used as add-on therapy.
For complete list of drugs used in Parkinson disease, see classification of antiparkinsonian agents
So let’s start our discussion with two main drug targets in PD.
1. Dopamine precursors - Levodopa
Levodopa is a dopamine analogue that is converted into dopamine within the CNS thereby improves dopaminergic transmission. In this way levodopa improves the motor performance in patients with Parkinson disease and highly efficient and considered as drug of choice.
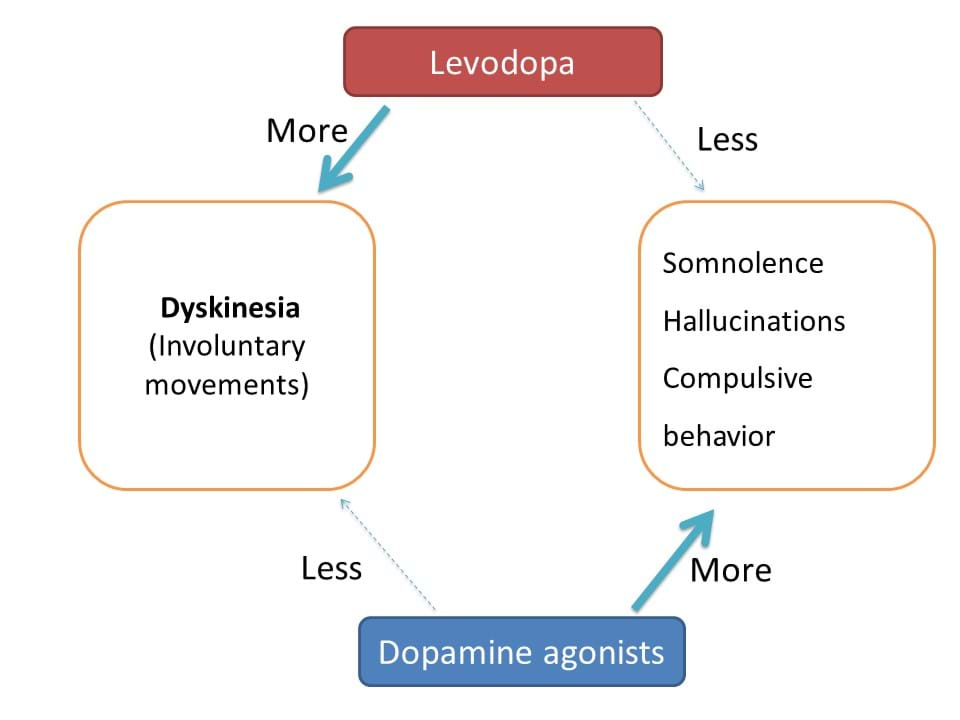
But levodopa also has another face. While it improves dopamine levels within the CNS, it is also associated with few of adverse effects related with high levels of dopamine. One of it's main adverse effect is bradykinesia which results in involuntary movements. Particularly these involutnary movements are more pronounced in patients with age below 60 years.
2.Dopamine agonists
Dopamine agonists such as bromocriptine, pramipexole, rotigotine and ropinirole are the alternative drugs for levodopa.
These drugs act directly on dopaminergic receptors and improve the dopaminergic effects eliminating motor disturbances in the Parkinson disease. These drugs are not associated with bradykinesia as observed with levodopa but may produce side effects like somnolence, hallucinations and complusive behavior. All these effects are due to enhanced activation of dopamine receptors by these drugs.
These side effects become more troublesome in patients with age above 60 years.
Conclusion
So, from the above discussion, we can draw two points.
- Levodopa is effective in any age group but show significant adverse effects in patients with age < 60 years.
- Dopamine agonists produce less dyskinesia but produce side effects that are more troublesome in age > 60 years.
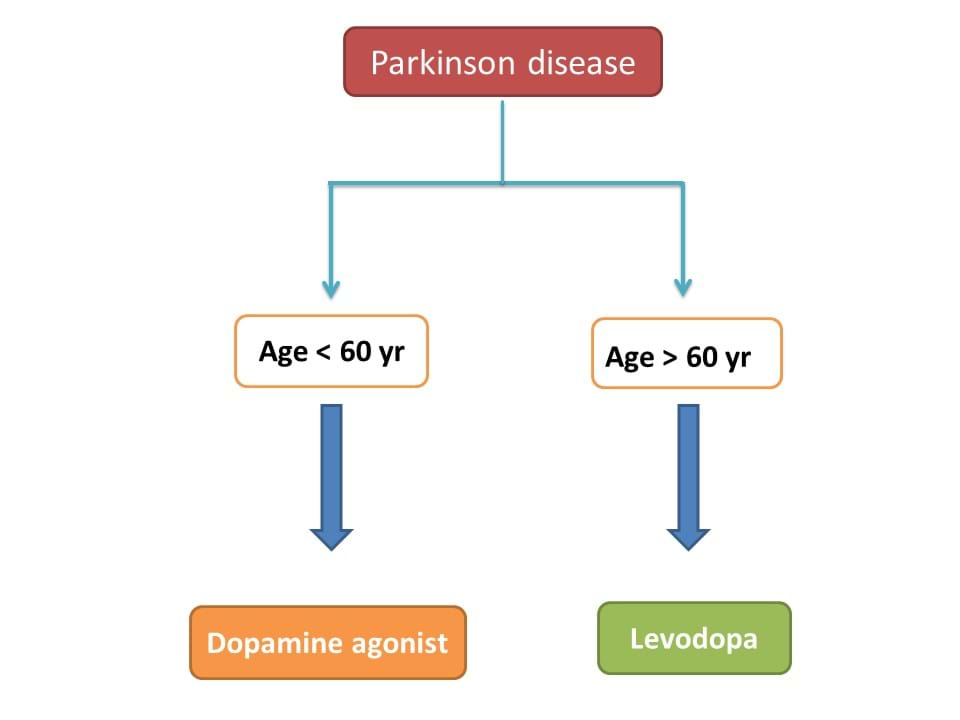
Hence it is recommended that dopamine agonists should be initiated in younger patients (age 55-60) and levodopa in older patients (age > 60).