Why cholestyramine should not be taken along with digoxin?
by egpat Posted on 22-08-2017
Cholestyramine is a bile acid binding resin that shows a drug interaction with digoxin. First of all, let’s discuss the how these drugs are acting.
High cholesterol levels particularly in the form of LDL cholesterol are severe risk factors for generation of atherosclerosis. So, important goal in prevention of atherosclerosis is to control the levels of LDL cholesterol and even increase HDL cholesterol.
What is the source of cholesterol in the body?
One of the main sources of the cholesterol is coming from diet. The cholesterol in the diet is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and stored in the liver. From the liver some amount of the cholesterol is secreted into the GI tract through the bile. Again the cholesterol can be reabsorbed from the GI tract by biliary reabsorption.
Another source of cholesterol in the body is from its biosynthesis within the liver.
Many drug targets are available to control the levels of cholesterol within the body and among them one class of drugs called statins act on liver effecting cholesterol biosynthesis. For complete mechanism, see how statins decrease cholesterol.
Two of the other drug targets act on gastric absorption of the cholesterol controlling levels of cholesterol entering into the body from diet.
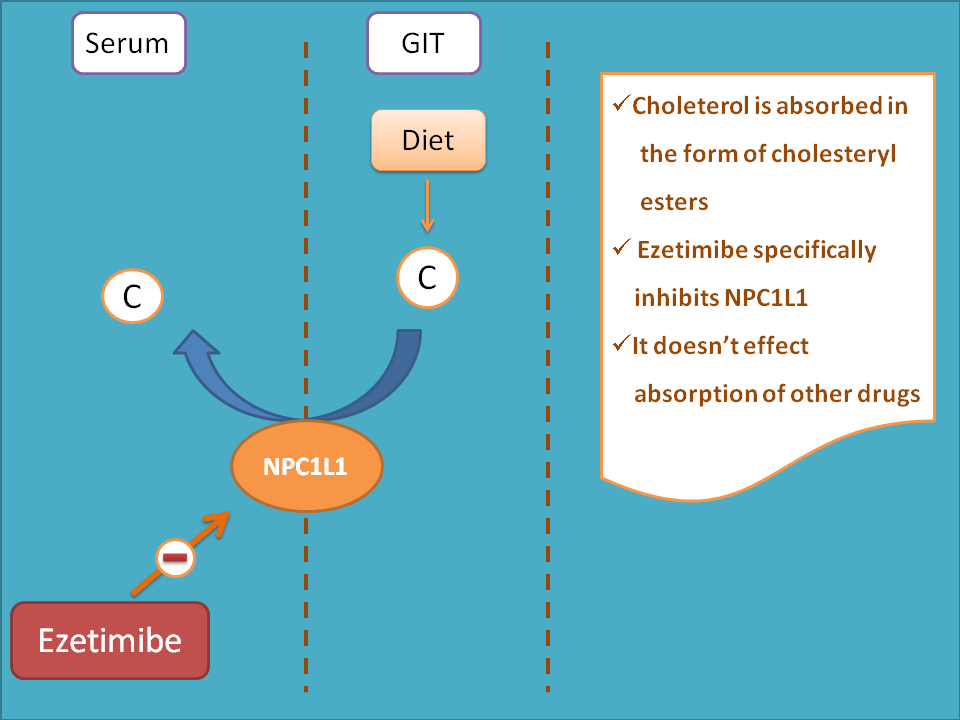
Of these two drug targets acting on absorption of cholesterol, drugs like ezetimibe inhibit cholesterol transporter protein within the brush border of the GI tract thereby inhibit cholesterol absorption from GI tract. These drugs are specific to cholesterol so that they affect the absorption of cholesterol only but not the other drugs.
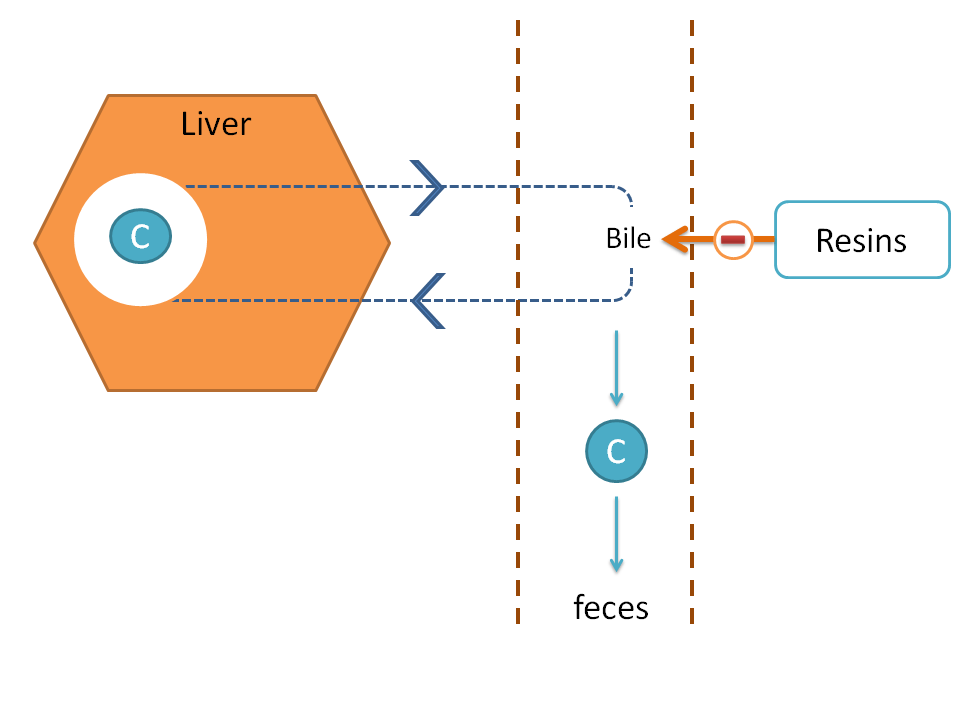
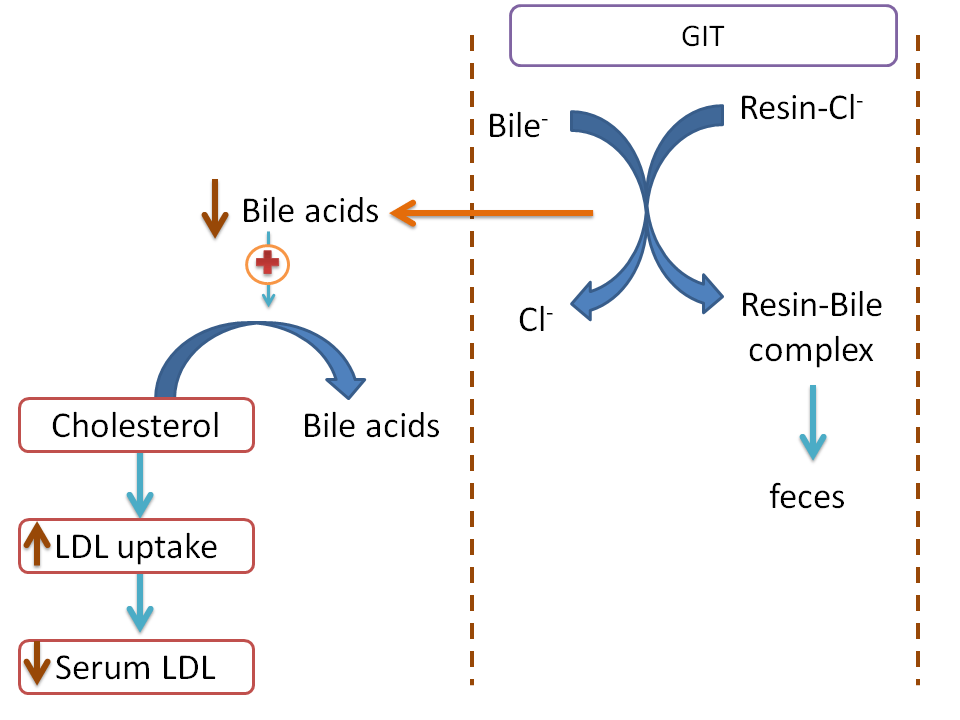
On the other hand, bile acid binding resins like cholestyramine and colestipol inhibit biliary reabsorption of cholesterol. These drugs are macromolecular resins that can form a complex with components of bile acid. These resins are made up of styrene-divinyl benzene copolymer which on substitution with quaternary ammonium groups acts as ion-exchange resin. Bile acids, in the form of slats, are negatively charged and exchanged with anion of these resins.

By this way, bile acids form a complex with bile acid binding resins which is insoluble, non-absorbable and finally excreted into the feces. This result in a decreased bile acid levels in the liver which then tries restore their level by converting cholesterol into bile acids. So, finally cholesterol levels in liver will fall. Now, liver also tries to restore its cholesterol levels. In this process, more number of LDL receptors are expressed on the liver enhancing LDL uptake into the liver. At the end, serum cholesterol levels fall.
Along with bile acids, few of the drugs like digoxin, aspirin, warfarin, tetracyclines are also excreted into the feces as their intestinal absorption is inhibited.
That’s why digoxin should not be given along with cholestyramine. As digoxin can absorbed within 1-2 hours, it can be given 1-2 hours before the administration of cholestyramine. Similarly cholestyramine resided at average for 4-6 hours within the intestine. Hence digoxin can be given after 4-6 hours of administration of cholestyramine.
Since cholestyramine interferes with absorption of digoxin, it can also be used at high dose for digoxin detoxification.