Why potassium levels should be monitored in patients using ACE inhibitors?
by egpat Posted on 08-06-2017
ACE inhibitors like Enalapril and ARBs like sartans produce renal failure leading to accumulation of potassium resulting in hyperkalemia. In this context, potassium supplements should not be given and serum potassium levels should be carefully monitored.
ACE inhibitors inhibit the conversion of angiotensin-I to angiotensin-II thereby inhibit the actions of angiotensin-II. The actions of angiotensin-II are sometimes beneficial and sometimes harmful and pathological to few disorders.
For example, AT II is a potent vasoconstrictor which is released during hypotension. Hypotension detected as decreased renal perfusion pressure activates rennin-angiotensin-system (RAS) which releases rennin from distal tubule. The released rennin then converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin-I which in turn then converted into AT II by ACE enzyme.

Now AT II acts on vascular smooth muscle to increase blood pressure and acts on heart to increase both rate and force of contraction. This restores the blood pressure to normal levels.
Important effect of angiotensin-II (AT II) on renal system
Glomerular filtration is the primary process at kidneys which initiates the filtration of small and soluble molecules going to filtrate. Large molecules like plasma proteins cann't pass through the membrane and they are retained.
The blood coming to glomerulus is supplied by afferent arterioles and blood going out of glomerulus is carried by efferent arterioles.
The rate of glomerular filtration depends on intraglomerular pressure which in turn depends on the pressure difference between efferent and afferent arterioles.
For an optimal glomerular filtration rate (GFR), afferent arterioles should have low pressure and efferent arterioles should have high pressure.
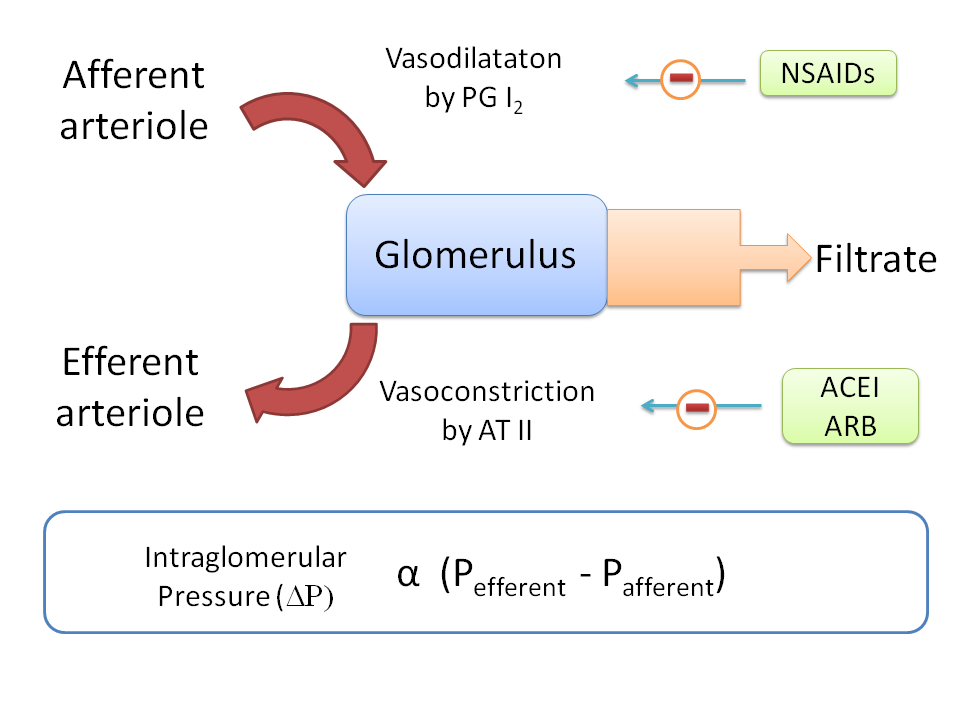
At afferent arterioles, prostaglandin I2 commonly called as prostacyclin maintains low blood pressure by vasodilatation.
Similarly at efferent arterioles AT II maintains high blood pressure by vasoconstriction.
If this physiological mechanism is disturbed by any drugs may lead to fall in GFR and subsequent renal failure on long term.
Two such drugs which effect renal function include NSAIDS acting on afferent arterioles and ACEI, ARBs acting on efferent arterioles.
Hence all these three category of drugs produce renal failure on long term.
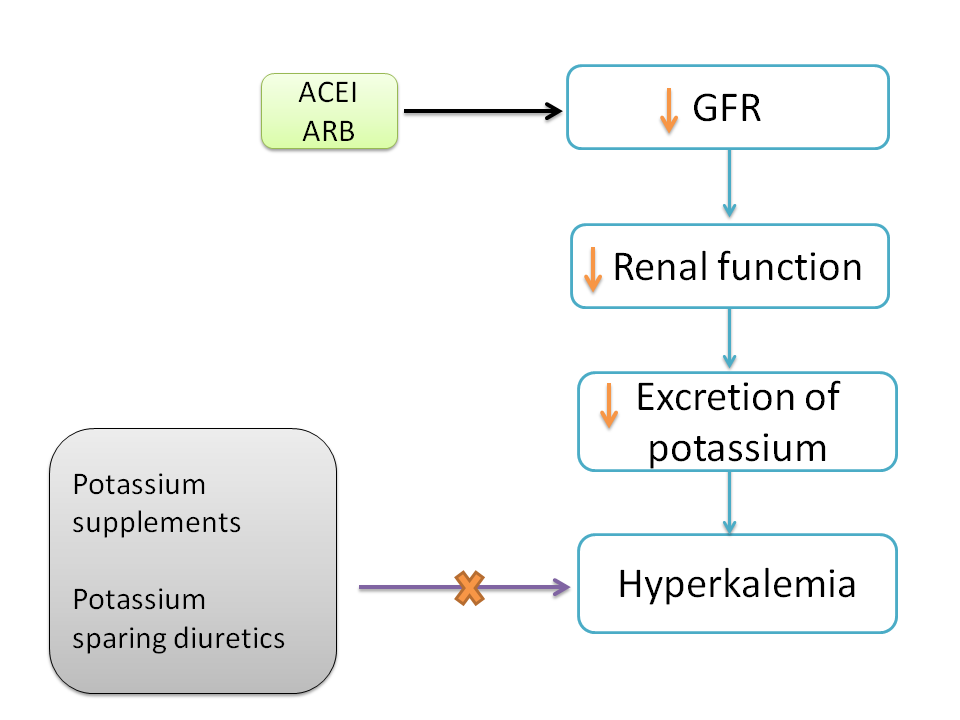
Particularly ACEI and ARBs decrease renal functionality leading to decreased excretion of potassium. This results in hyperkalemia.
So in such cases where the ACE inhibitors or ARBs are given for long term, the serum potassium levels should be closely monitored.