Why Verapamil contraindicated in Wolf-Parkinson-White syndrome?
by egpat Posted on 10-06-2017
Wolf-Parkinson-White syndrome is a hereditary disorder of abnormal conduction with unidirectional conduction block.
Unidirectional block produces conduction block only in one direction but allows impulses in another direction.
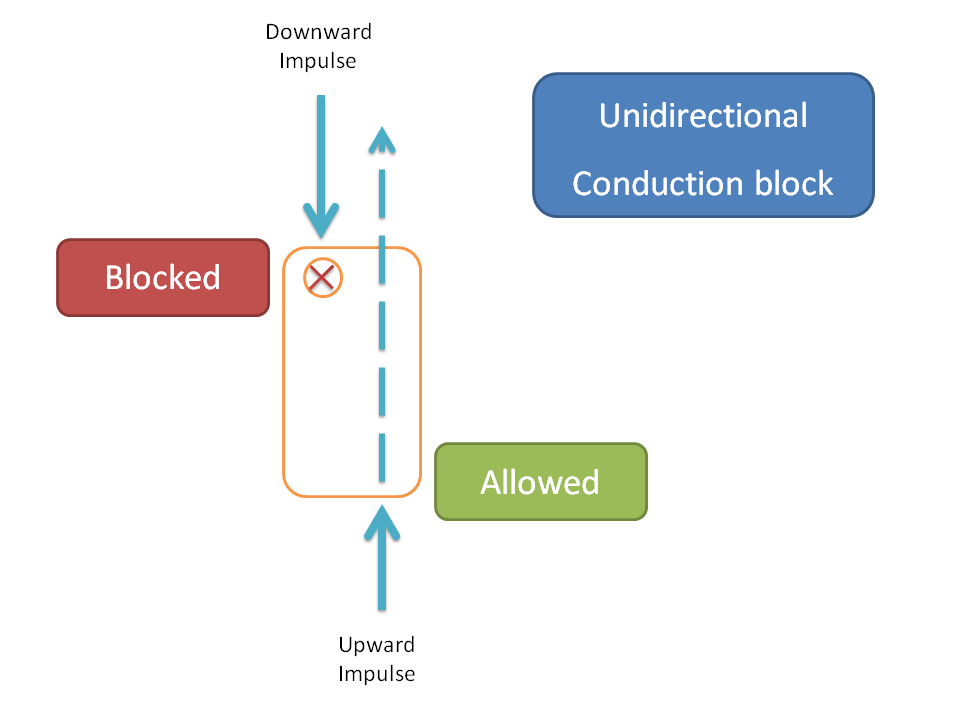
Due to unidirectional block impulse can pass through the blocked area in one direction activating cells one more time from opposite direction.
Suppose an impulse reaches a cell by time T1 and same impulse reaches the cell trough circulary pathway in opposite direction by time T2 . So the cell is getting two impulses one at time T1 and another at time T2 and the time interval between two impulses is T2-T1.
Normally a cell can be re-excited when it completes repolarisation. The minimum time period required to re-excite cell is called as effective refractory period (ERP).
So if an impulse reaches the cell before effective refractory period i.e. T2-T1 < ERP it will not produce any extra heart beat but if it reaches after ERP i.e. T2-T1 > ERP, it can produce an extra heart beat.
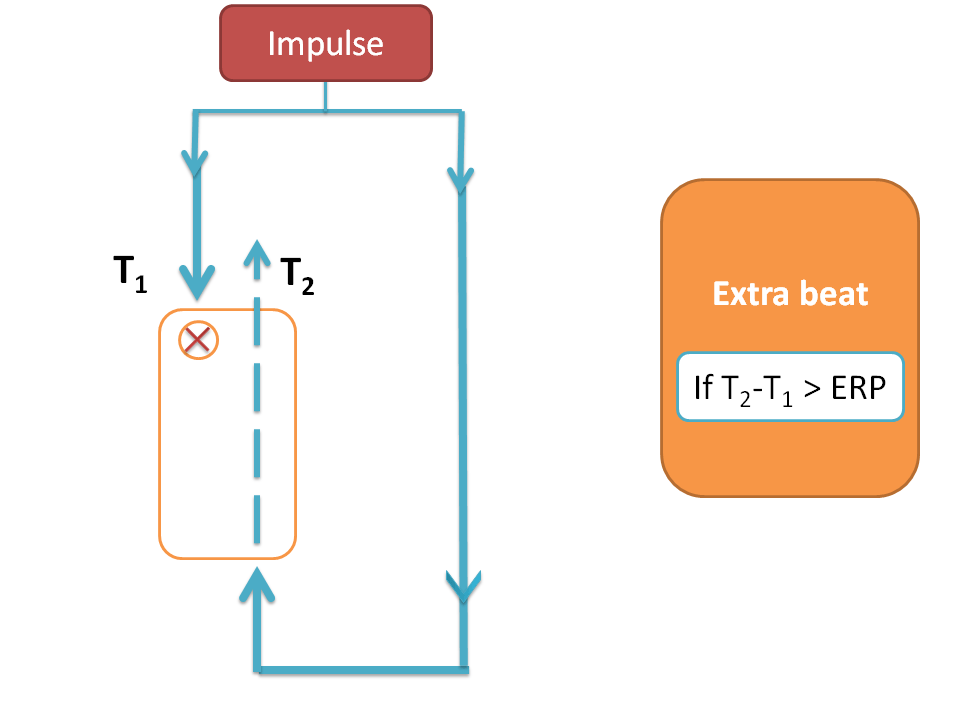
In re-entry the impulse reaches the cells in opposite direction after their refractory period generating one more heart beat.
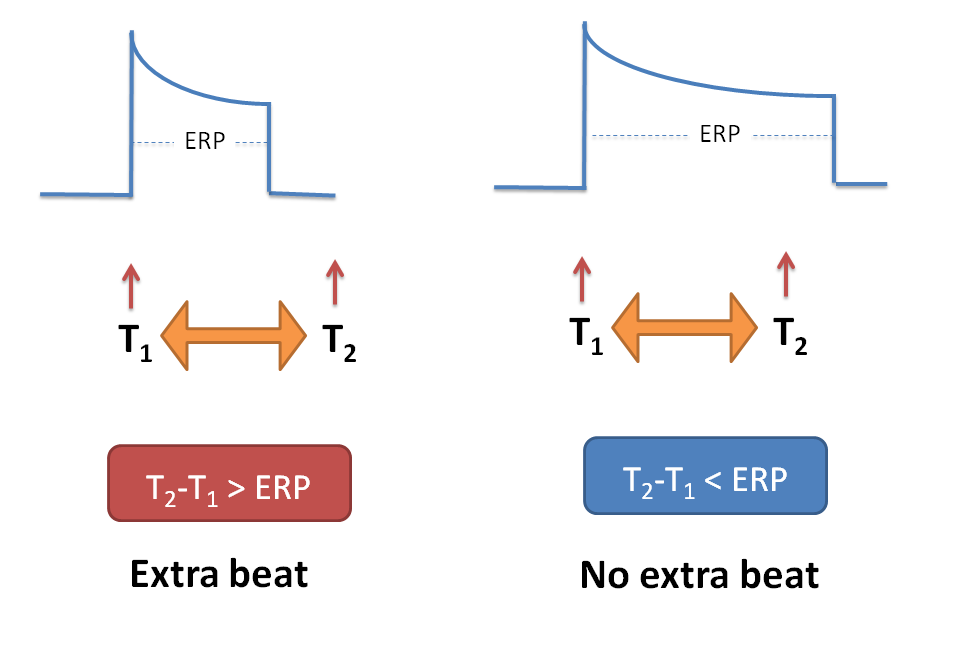
Since no extra beat can be observed if impulse re-enters into the cell before refractory period, drugs which increase effective refractory period (ERP) are of choice in re-entry type of arrhythmias.
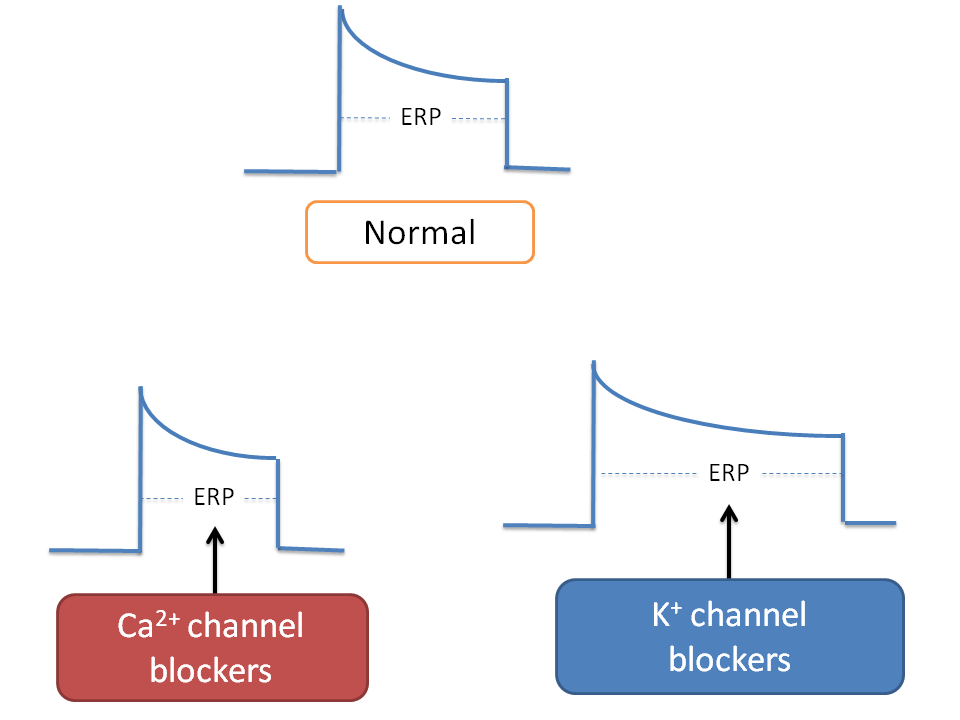
Potassium channel blockers increase plateau phase thereby increase ERP hence indicated for re-entry.
On the other hand, calcium channel blockers like verapamil decrease the ERP hence may increase re-entry type of arrhythmia. Therefore verapamil is contraindicated in WPW.