Beta blockers with additional actions
Beta blockers can also show additional activities which may add to their cardiovascular effect and improve therapeutic response. These additional properties of beta blockers can be categorized into four types such as
- Partial agonist activity
- Membrane stabilising activity
- Vasodilatory activity
- Alpha blocker activity
Partial agonist activity
Drugs binding to the receptors can produce response in various ways as agonist or antagonist or sometime as partial agonist. Agonists are the drugs that bind to beta receptors produce similar action like catechol amines. Similarly antagonist is a drug that binds to the receptor and prevents the action of catechol amines.
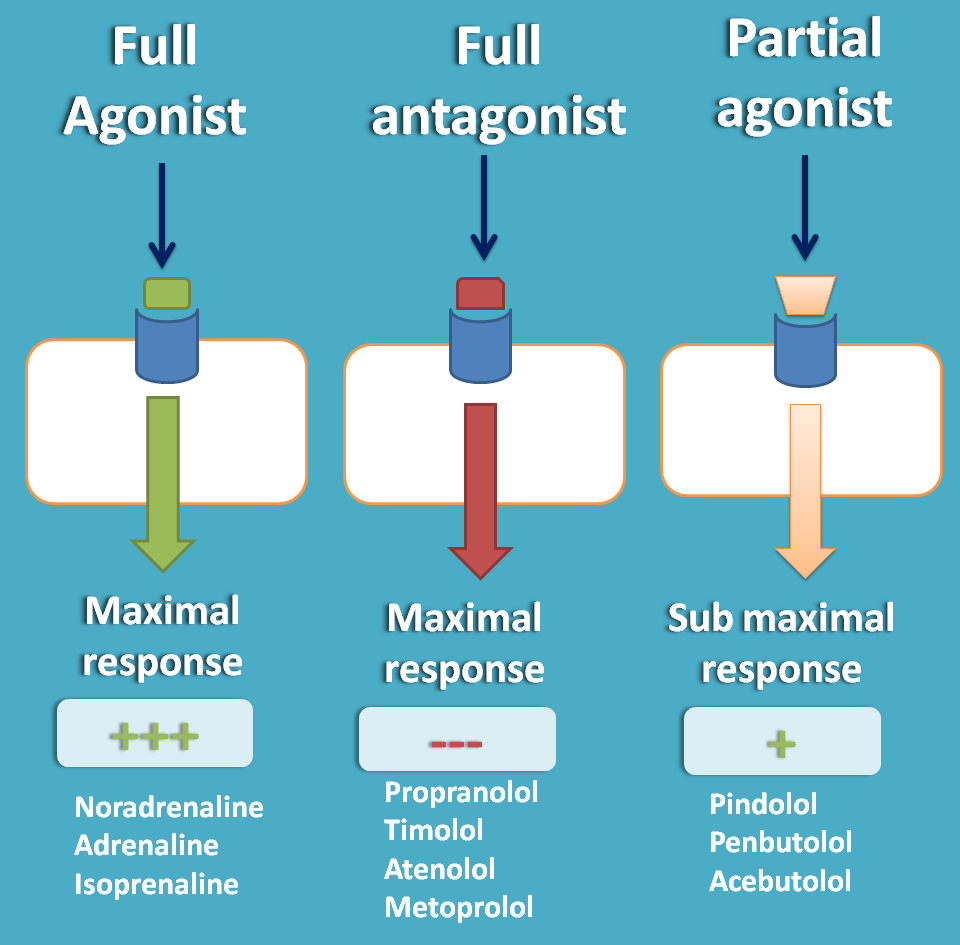
Partial agonist combines above two characters. It binds to the receptor and act like agonist but prevents binding of catechol amine just like antagonist.
In this way, these drugs stimulate beta receptors at low level. Pindolol and penbutolol are partial agonists in non-selective beta blockers and acebutolol in selective beta blockers.
Membrane stabilising activity
These are the drugs that not only antagonise the beta receptors but also modify the membranes response so that they are stabilized and can’t respond to the catechol amines.
Ex: Propranolol
Vasodilatory activity
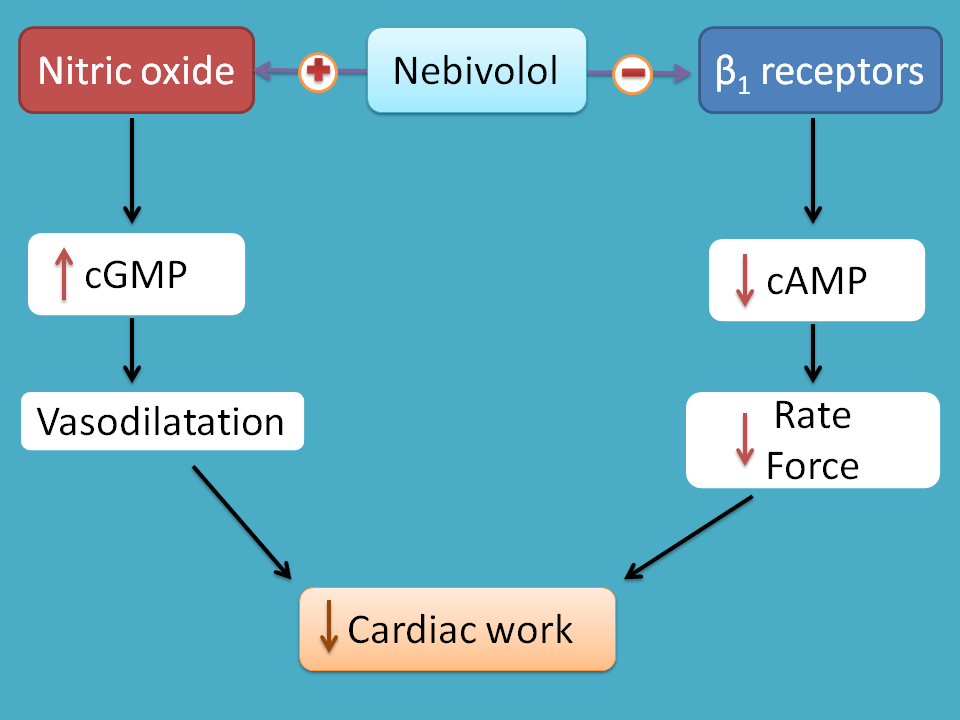
Nebivolol is such a beta blocker which blocks beat receptors at the same time release nitric oxide from endothelium. The released nitric oxide then activated cGMP in vascular smooth muscle which produces relaxation.
Alpha blocker activity
These drugs are also called as alpha and beta blockers. They act as antagonist at both the receptors. Alpha block produces direct vasodilatation whereas beta block inhibits cardiac stimulation by catechol amines.
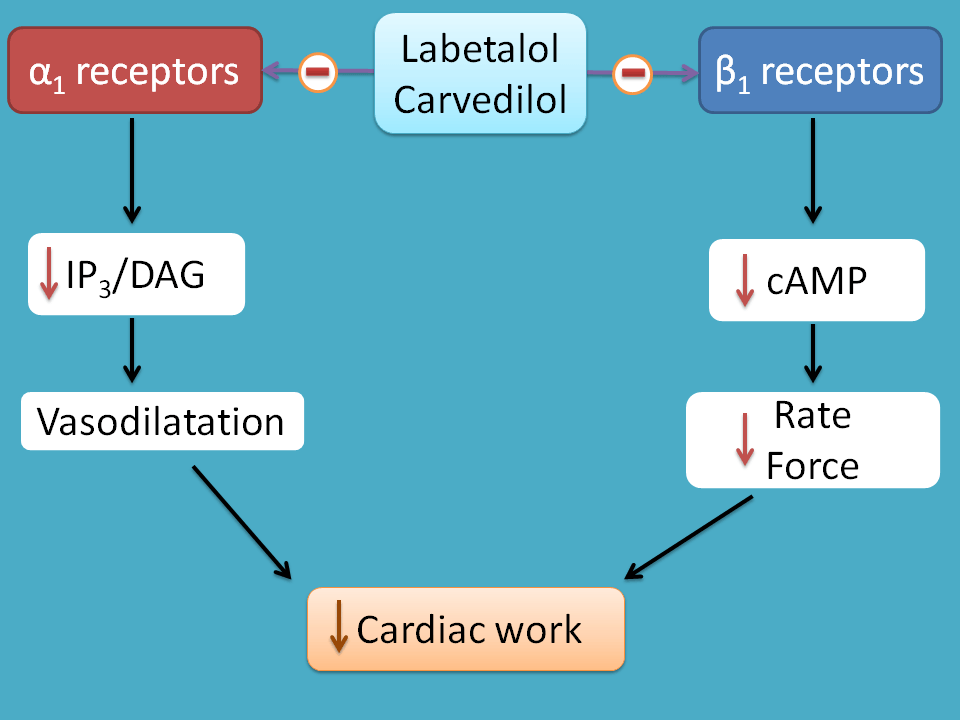
Both the actions finally decrease blood pressure hence these drug are useful in treatment of hypertension.
Carvedilol is such a drug used in hypertension associated with heart failure.

Similarly labetalol is another drug used in the treatment of hypertension during pregnancy.