Sympathetic divsion
Now let's see anatomical features of sympathetic division.
Location of ganglia
Quite opposite to the parasympathetic system, sympathetic ganglia lies close to the spinal cord.
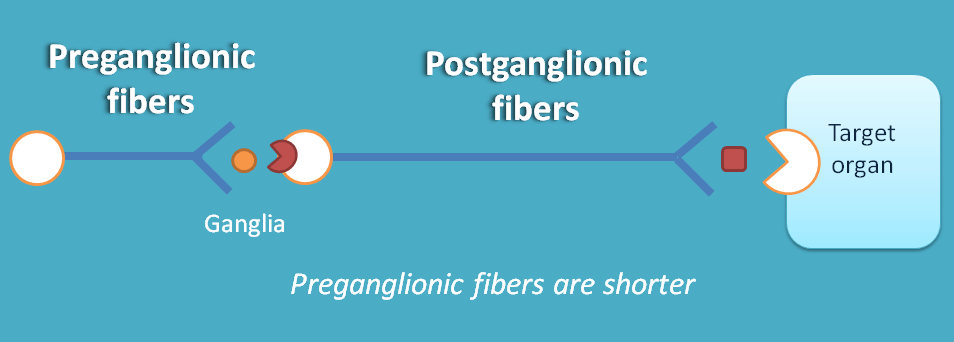
Hence the length of preganglionic fibers are shorter than that of post ganglionic fibers.
Outflow
Sympathetic out flow is called as Thoraco-Lumbar out flow as the preganglionic fibers emerge from cell bodies located in thoracic and lumbar segments of spinal cord.
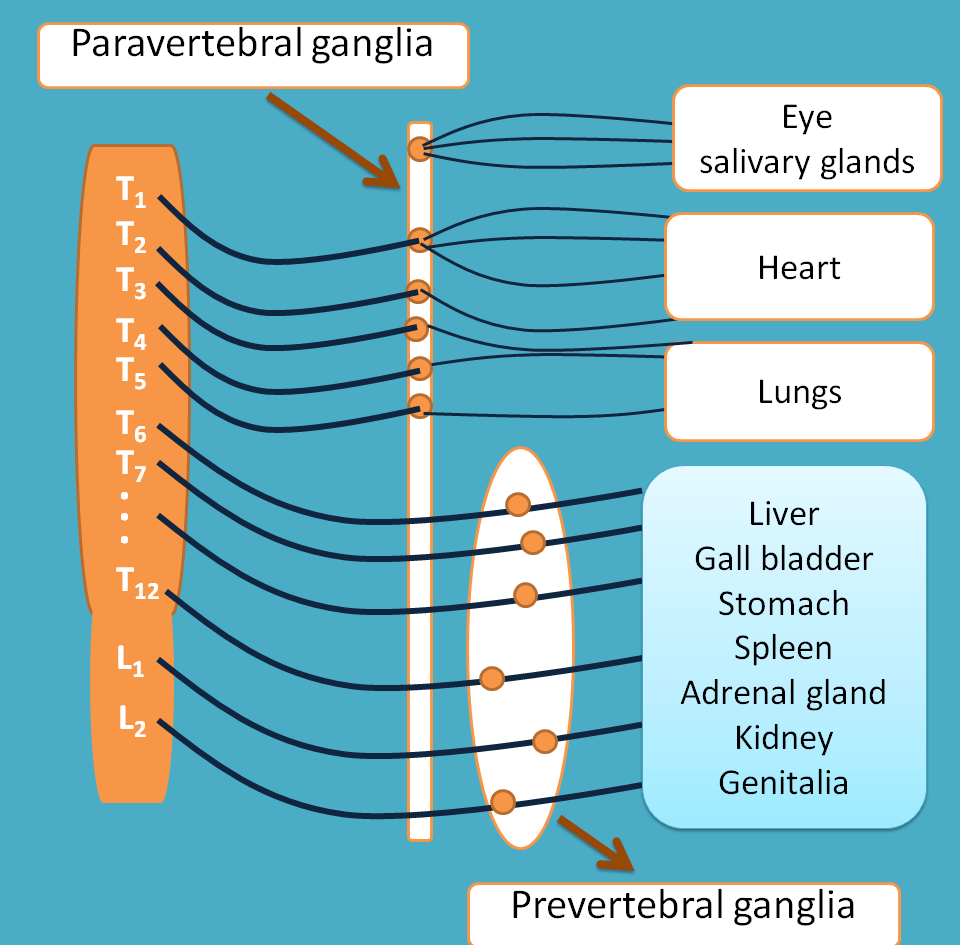
Here preganglionic fibers can form ganglia in three ways.
- Paravertebral ganglia
- Prevertebral ganglia
- No ganglia
Paravertebral ganglia
The preganglionic fibers emerging from T1 to T5 segments of spinal cord form a chain like ganglia mainly supplying to the above thoracic organs.
This outflow supplies to the various organs including
- Eye
- Lacrimal glands
- Salivary glands
- Sweat glands
- Nasal mucosa
- Blood vessels
- Heart
Prevertebral ganglia
The preganglionic fibers emerging from T5 to L2 segments of spinal cord form a separate ganglia called prevertebral ganglia and supply to the abdominal and pelvic organs.
Organs supplied by this outflow include
- Stomach
- Liver
- Spleen
- Small intestine
- Large intestine
- Kidney
- Rectum
- Genitalia
- Urinary bladder
No ganglia
Sympathetic fibers supplying to adrenal medulla don't form any ganglia and directly end with in the medullary cells that secrete two hormones adrenaline and norepinephrine
Is acetylcholine required for sympathetic response?