- Home >
- Test papers >
MCQ on antibacterials: Page-2

(A) S
(B) Q
(C) P,R
(C) Q,S
Moxifloxacin is a fluoroquinolone acts by inhibition of topoisomerase II.
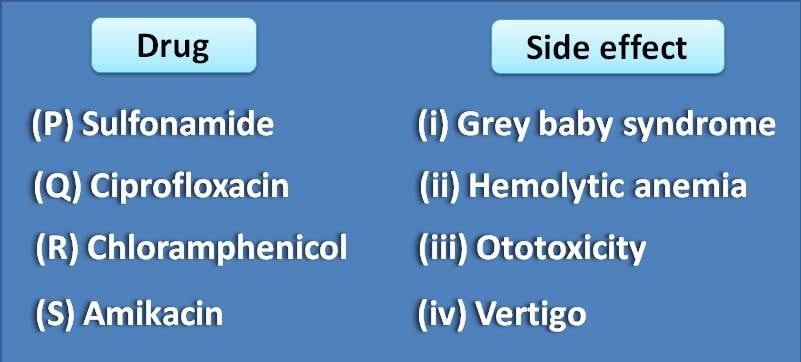
(A) P-ii, Q-iii, R-i, S-iv
(B) P-iii, Q-ii, R-iv, S-i
(C) P-iv, Q-i, R-iii, S-ii
(D) P-ii, Q-iv, R-i, S-iii
Sulfonamides produce haemolytic anaemia. Ciprofloxacin produces vestibular disorders. Black water fever is produced by quinine, an antimalarial agent. Amikacin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic that produces ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity.
(A) Cisplatin, nausea and vomiting
(B) Trimethoprim. Megaloblastic anaemia
(C) Chloramphenicol, grey baby syndrome
(C) Cefalosporins, ototoxicity
ototoxicity is produced by aminoglycosides. Cefalosporins produce allergic reactions like penicillins.
(A) Amoxicillin
(B) Methenamine
(C) Ciprofloxacin
(D) Vancomycin
(A) Chloramphenicol
(B) Gentamycin
(C) Tetracycline
(D) Ciprofloxacin
Chloramphenicol inhibits ATP synthesis in host resulting in bone marrow depression which can lead to cyanosis. In neonates, the drug is accumulated as there is insufficient development of conjugation and excretion leading to pronounced cyanosis and grey discoloration of the baby.