Beta adrenergic receptor agonists
β1- agonists
Dobutamine is a β1 adrenergic receptor agonists that specifically acts on cardiac muscle increasing both rate and force of contraction. It increases cAMP levels within the cardiac muscle which stimulates protein kinases increasing intracellular calcium levels. This results increased force of contraction.
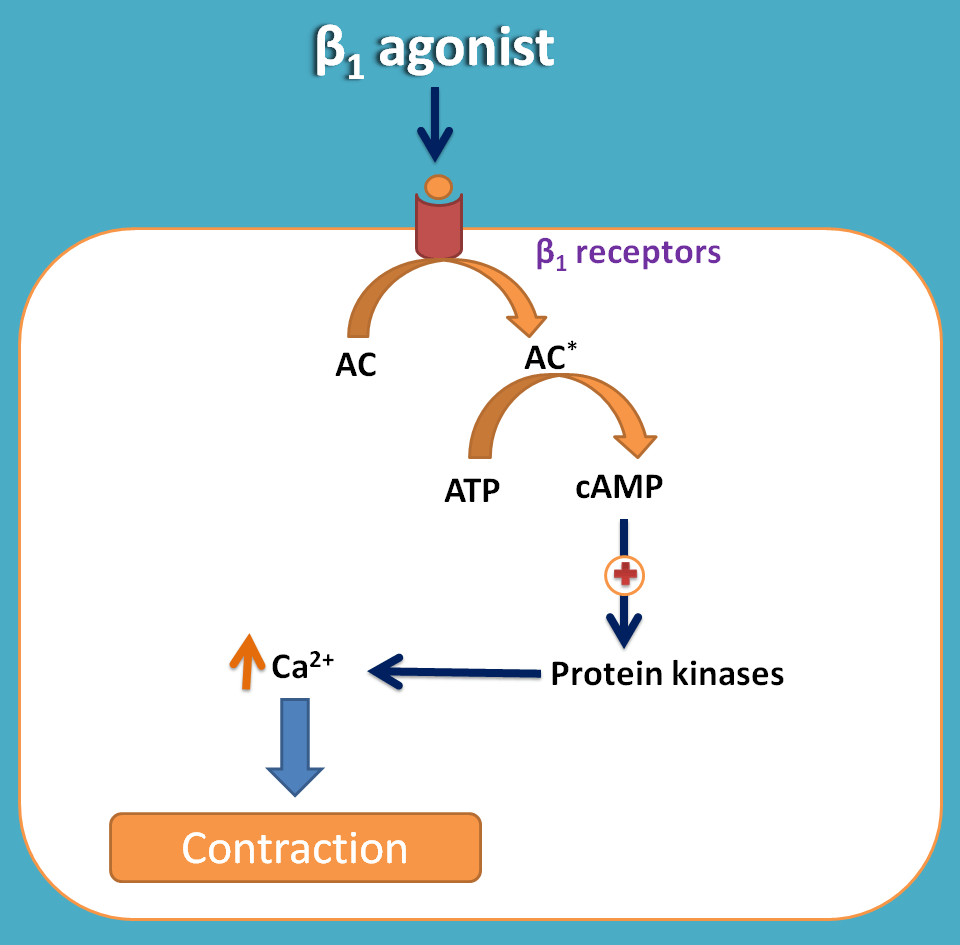
Two advantages of dobutamine are
- It is selective for β1 adrenergic receptors
- It doesn’t increase cardiac oxygen consumption
Side effects
Many of the side effects are due to its cardiac stimulatory action.
- Palpitations
- Headache
- Nervousness
- Rapid heartbeat
- Increased blood pressure
- Nausea
Indications
Dobutamine can be used in two conditions
- Congestive heart failure
- Cardiogenic shock
β2- agonists
Again these drugs are specific to the β2 adrenergic receptors particularly acting on bronchioles producing relaxation. Four drugs are available in this category including
- Terbutaline
- Salbutamol
- Salmeterol
- Formoterol
Already we have discussed the two structural modifications responsible for β2 selectivity that can be observed in these drugs. Terbutaline has resorcinol hydroxyl groups and whereas salbutamol and salmeterol have have hydoxymethyl group at 3rd position. Formoterol has entirely different formyl group at 3rd position.
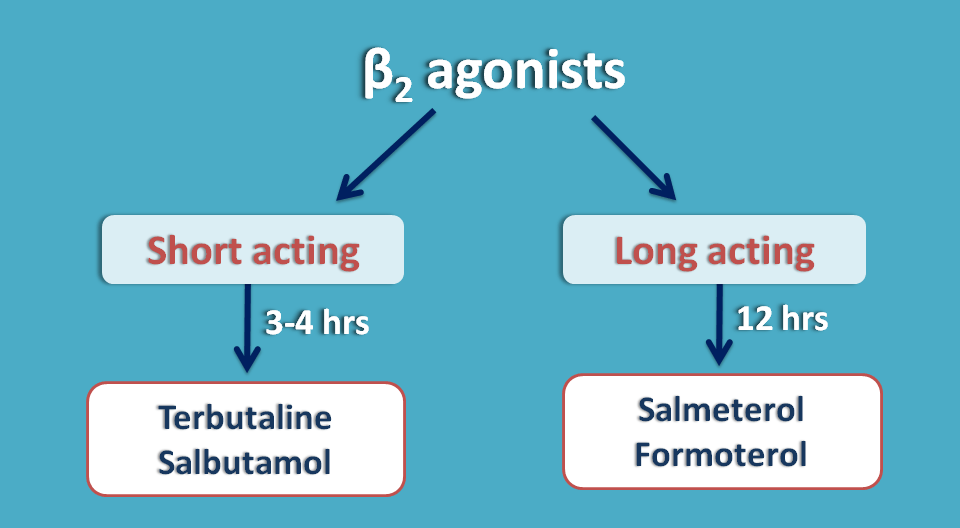
Terbutaline and salbutamol are short acting bronchodilators with duration of action is around 3-5 hrs. On the other hand, salmeterol and formoterol are long acting with duration of action about 12 hrs.
Why salmeterol is long acting?
One more structural modification within this class is alkyl substitution on aliphatic amine.
As the chain length of alkyl group in amine increases, the duration of action of β2 agonists increases.
Terbutaline and salbutamol have tertiary butyl groups on nitrogen whereas salmeterol and formoterol have more lipophilic carbon chain hence long acting.
How they act?
These drugs selectively bind to the β2 receptors thereby increase cAMP within the cell. This increase cAMP causes phosphorylation of myosin-light chain kinases (MLCK) which are actually required for contraction.
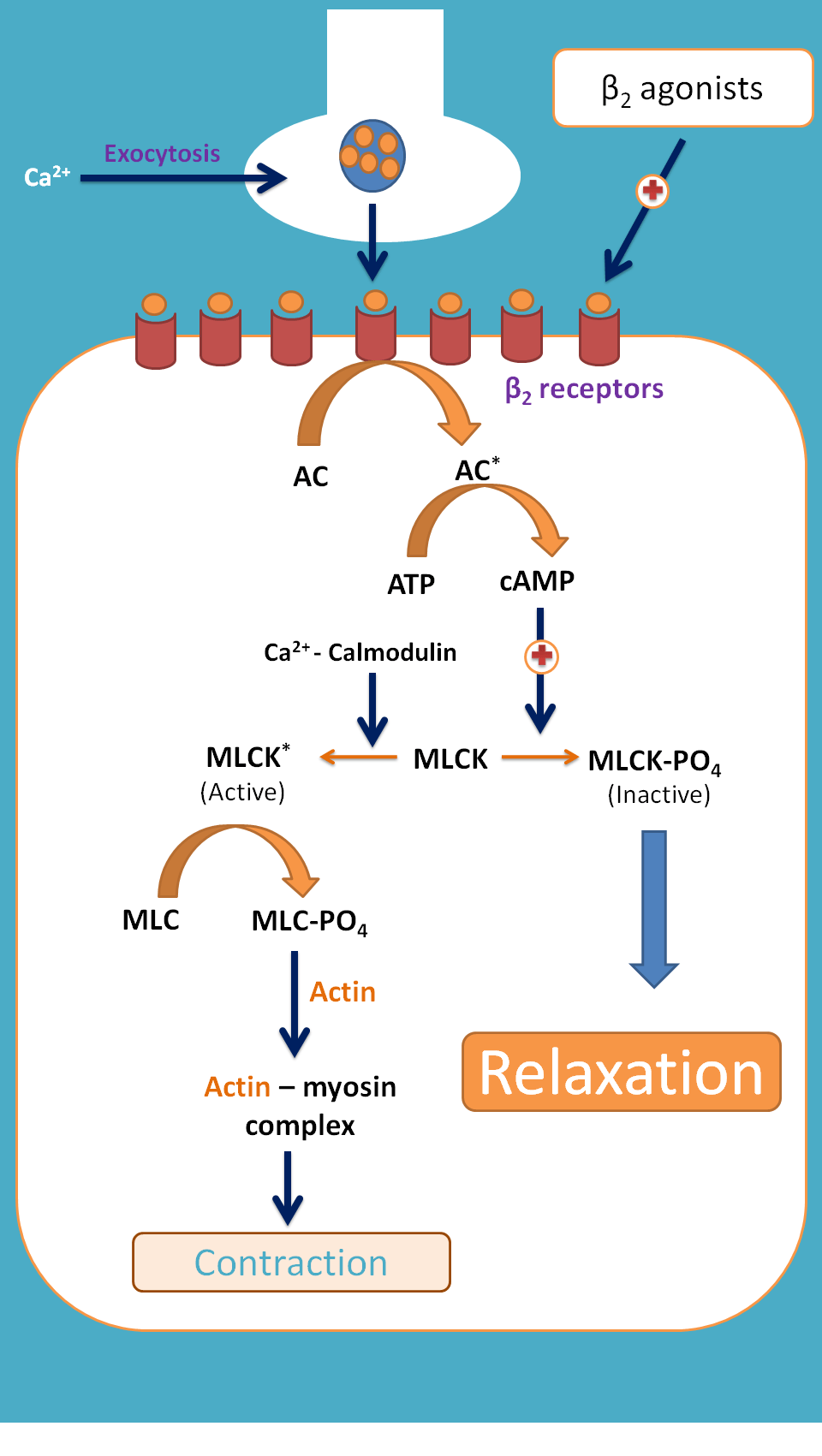
As MLCK is phosphorylated, it becomes inactive preventing contraction. This results in relaxation of bronchial smooth muscle.
Side effects
Side effects are less when they given by inhalation route due to less systemic absorption.
Eventhough some amount of the drug reaches into systemic circulation producing following effects.
- Tachycardia
- Tremors
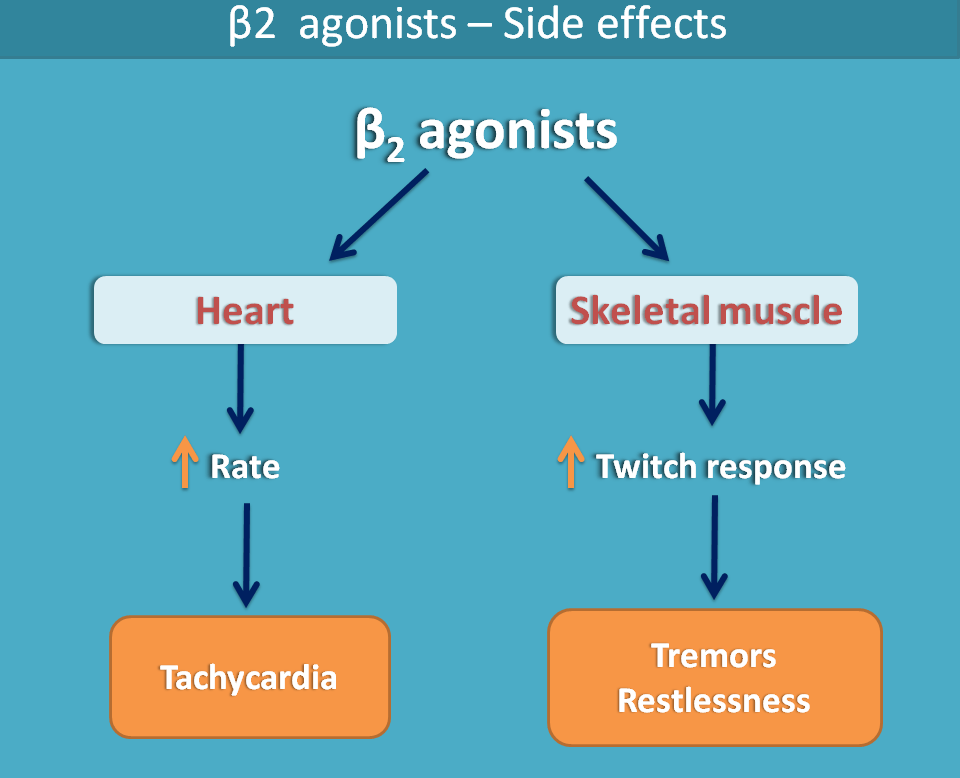
Tachycardia is due to action of these drugs on β1 receptors. Tremor is a repeated contraction skeletal muscle which is increased by β2 agonists as hey increase blood flow thereby enhance twitch response of skeletal muscle.
Indications
These drugs are mainly used as bronchodilators in
- Asthma
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD)
- Exercise induced bronchospasm
Salbutamol also relaxes uterine in pregnant woman hence used to delay the labor in premature pregnancy.