Beta adrenergic receptors
β-adrenergic receptors can be sub classified into β1, β2 and β3 receptors. All these receptors are G-protein coupled receptors linked to activation of adenylyl cyclase and increase cAMP.
β1 adrenergic receptors
β1 receptors are mainly present at
- Heart
- Kidney
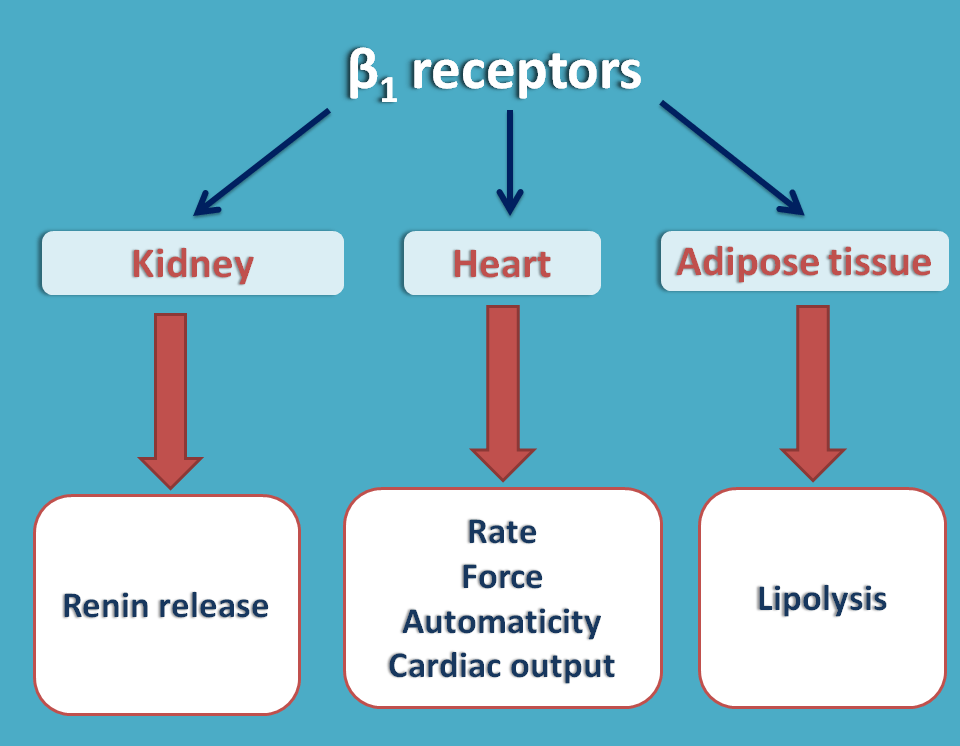
Their main location is heart where they produce
- Positive inotropic effect - Increase in force of contraction
- Positive chronotropic effect – Increase in rate of contraction
- Increase automaticity
On the kidney, β1 receptors are present on juxtagolmerular cells and responsible for release of renin.
β2 adrenergic receptors
The main locations of β2 adrenergic receptors are
- Smooth muscle
- Vascular smooth muscle
- GI smooth muscle
- Uterine
- Bronchioles
- Glands
- Salivary glands
- Liver
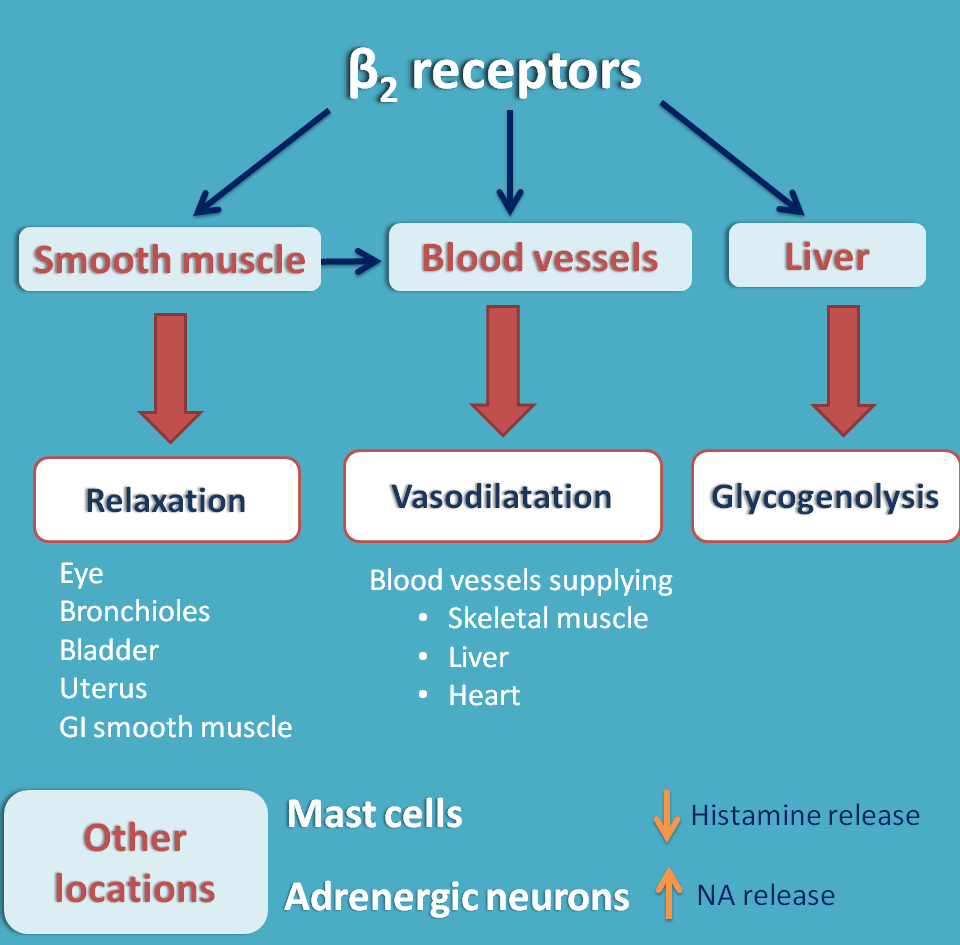
For example, on vascular smooth muscle both the receptors are present but α1 receptors are predominantly acting.
On the other hand, vascular smooth muscle supplying to skeletal muscle and liver are predominantly acting by β2 receptors leading to vasodilatation.
At GI smooth muscle both the receptors produce relaxation.
Just like α1 receptors, β2 receptors increase salivary secretion and glycogenolysis in liver.
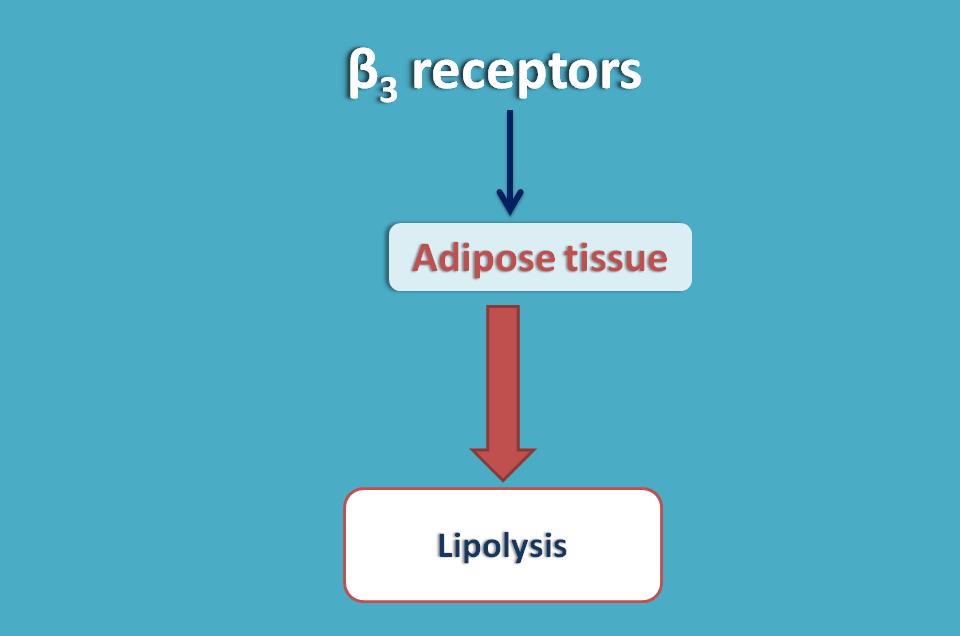
β3 adrenergic receptors
β3 adrenergic receptors are mainly located in adipose tissue where they are responsible lipolysis, the breakdown of the fat.