Muscarinic receptors
Now let’s see muscarinic receptors. Muscarinic receptors are sub classified into 5 types from M1 to M5.
Nature of receptor
All muscarinic receptors are G-protein coupled receptors and can be categorised into two groups based on the type of receptor.
- Excitatory - M1, M3 and M5 receptors
- Inhibitory - M2 and M4 receptors
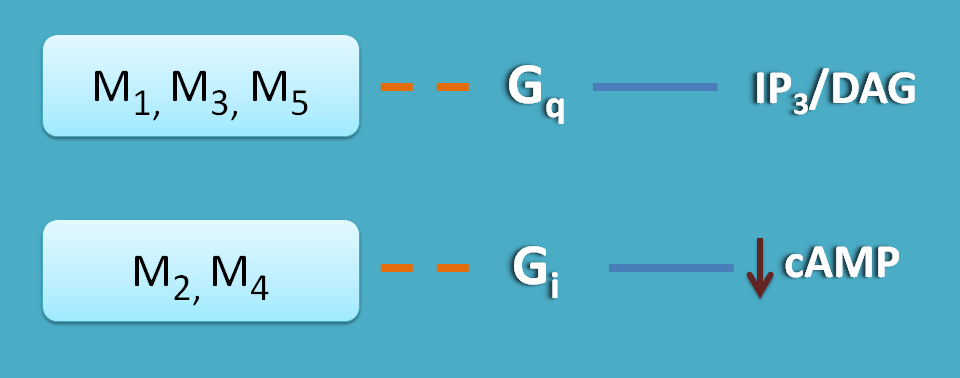
Excitatory muscarinic receptors are of Gq type coupled with IP3/DAG as secondary messengers whereas inhibitory muscarinic receptors are of Gi type coupled with decrease in cAMP.
M1, M3 and M5 receptors activate phospholipase C and thereby release IP3 and DAG whihc increase intracellular calcium levels. This results in excitation and contraction in smooth muscle.
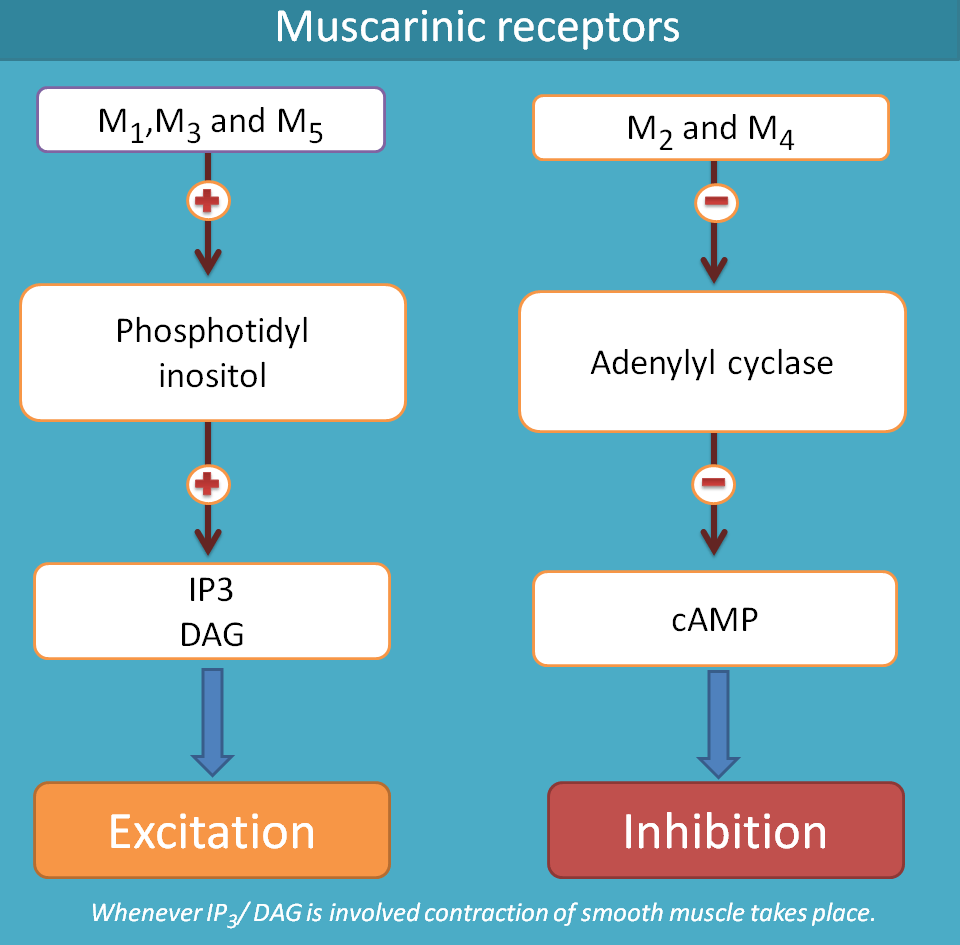
Similarly M2 and M4 receptors are coupled with inhibition of adenylyl cyclase system which actually converts ATP into the secondary messenger cAMP. As cAMP is required for activation of protein kinases and intracellular actions, a fall in cAMP levels in the organ leads to inhibition.
Location
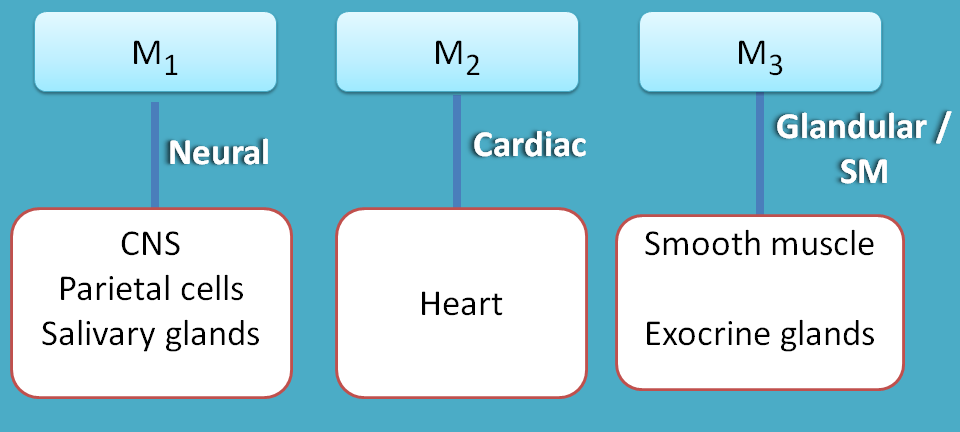
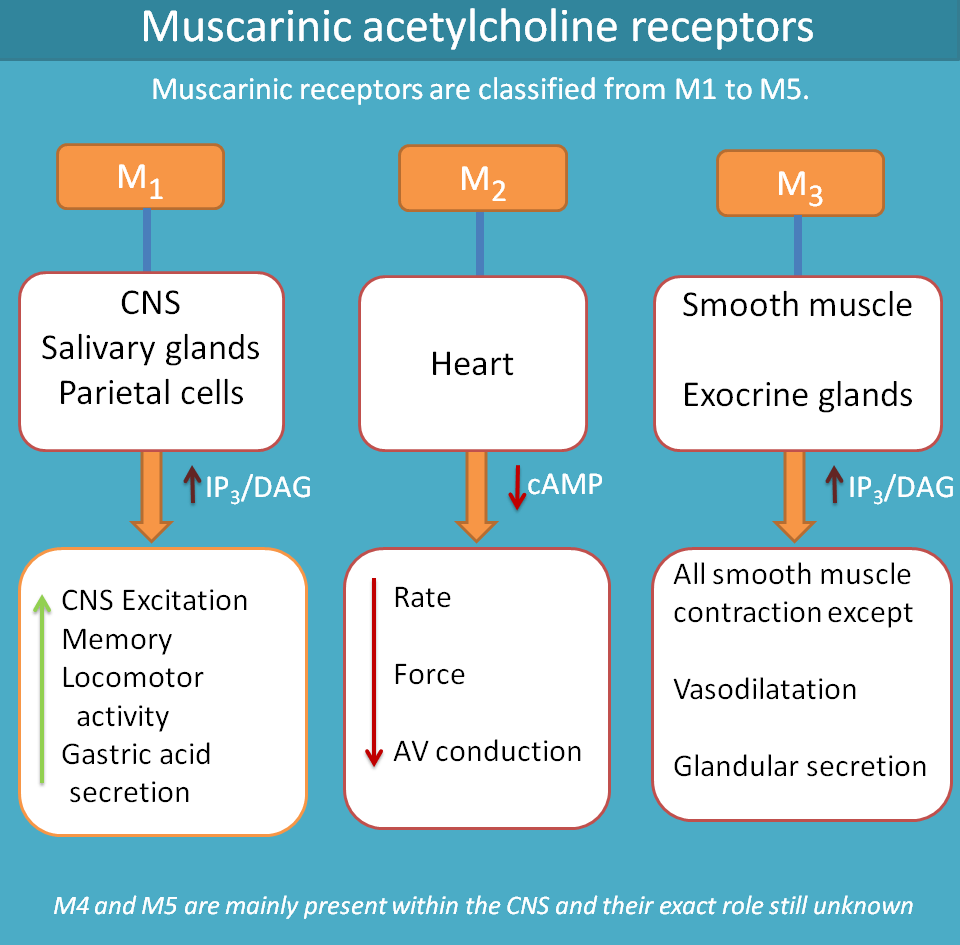
M4 and M5 are mainly present within the CNS and their functional role is not exactly known and still research is going. So we focus more on M1, M2 and M3.
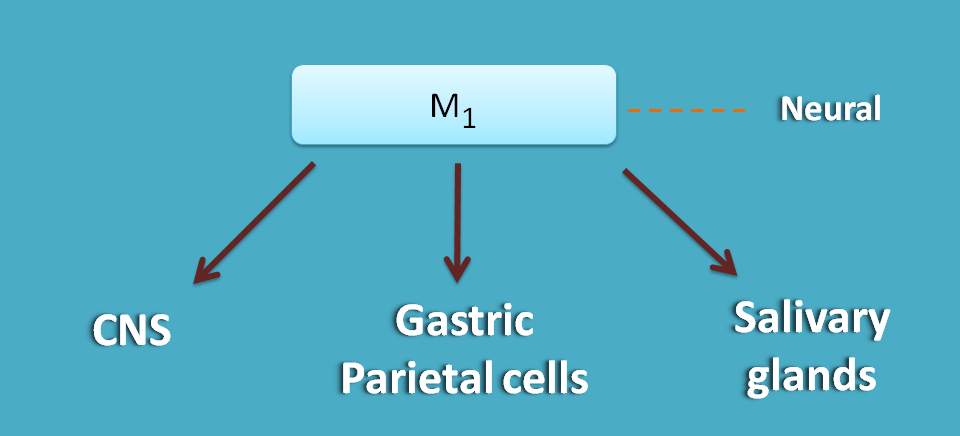
M1 receptors are present at three locations.
- CNS
- Gastric parietal cells
- Salivary glands
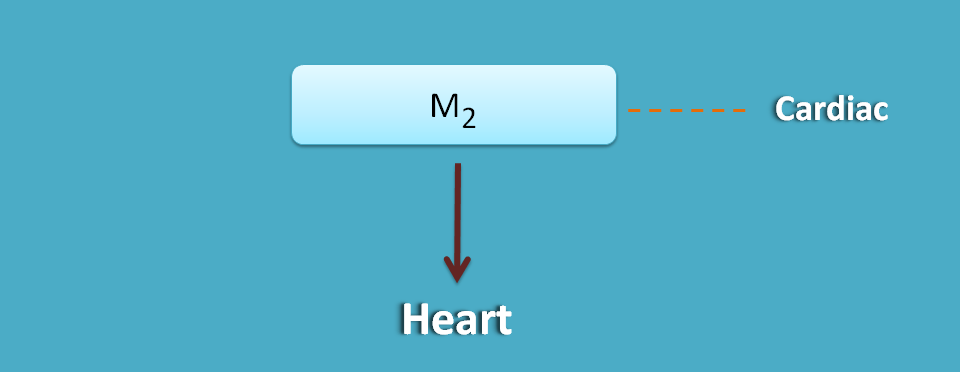
M2 are mainly on present on the heart hence they are called as cardiac receptors.
M3 receptors are located on exocrine glands and smooth muscle.
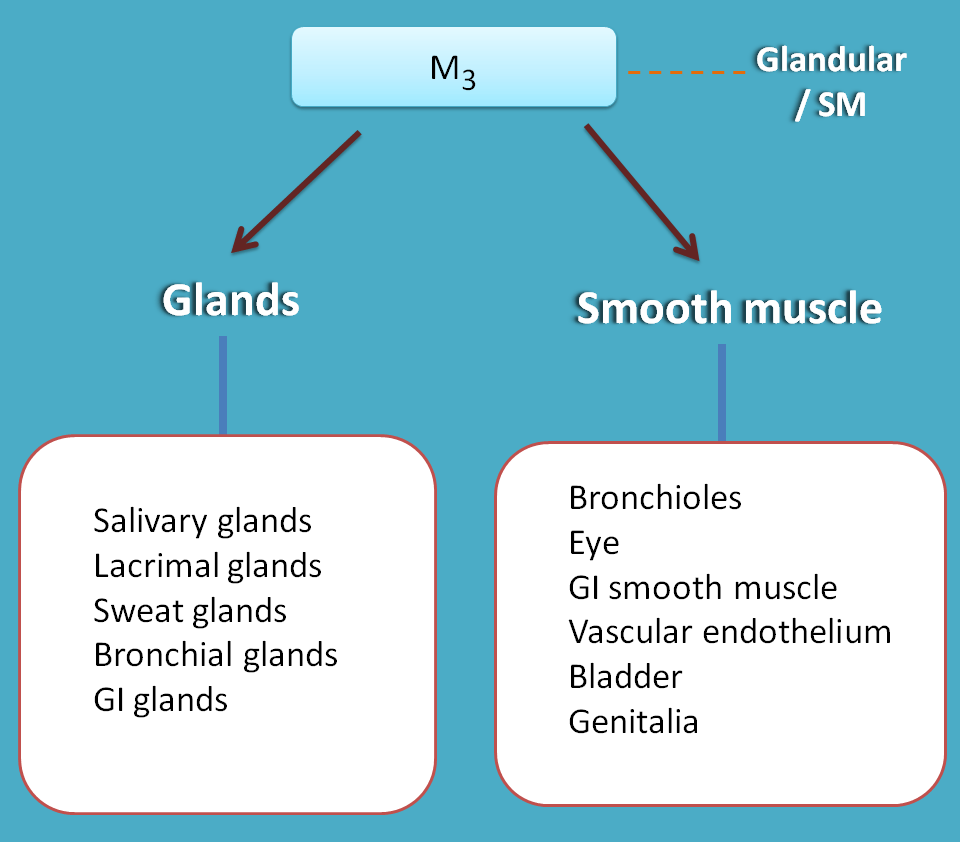
The main locations include
- Glands
- Lacrimal glands
- Salivary glands
- Sweat glands
- Bronchial glands
- gastric glands
- Smooth muscle
- Bronchioles
- Eye
- GI smooth muscle
- Vascular endothelium
- Bladder
- Genitalia
Function
Now let's see the function of muscarinic receptors and keep one fact in mind that M1, M3 and M5 are excitatory while M2 and M4 are inhibitory.
M1 receptors
As the main location of M1 receptors is CNS, they mainly produce CNS stimulation.
- CNS excitation
- Increase in memory
- Increase in locomotor activity
- Gastric acid secretion
- Salivary secretion
Since M1 receptors are responsible for memory, muscarinic blockers like hyoscine produce amnesia (short-term loss of memory).
M2 receptors
M2 receptors are mainly present on heart and produce cardiac inhibition.
- Decrease rate of contraction
- Decrease in force of contraction
- Decrease in AV conduction
M3 receptors
M3 receptors are mainly produce contraction of smooth muscle and secretion of exocrine glands
- Smooth muscle
- Pupilary constriction
- Broncho constriction
- Increase in GI motility
- Bladder constriction
- Vasodilatation
- Exocrine glands
- Salivary secretion
- Lacrimal secretion
- Bronchial secretion
- Gastric secretion
- Sweat secretion