Classification
The main goal of adrenergic agonists is to increase adrenergic transmission acting either directly or indirectly.
Based on the type of interaction they can be classified in to three types.
- Directly acting
- Indirectly acting
- Mixed acting
Directly acting
These drugs directly bind to the adrenergic receptor and increase adrenergic transmission.
Based on the structure they can be of two types.
- Catechol amines
- Non-catechol amines
Catechol amines
Drugs in this category include
- Epinephrine
- Norepinephrine
- Dopamine
- Isoprenaline
Except isoprenaline, all catechol amines are endogenous mediators.
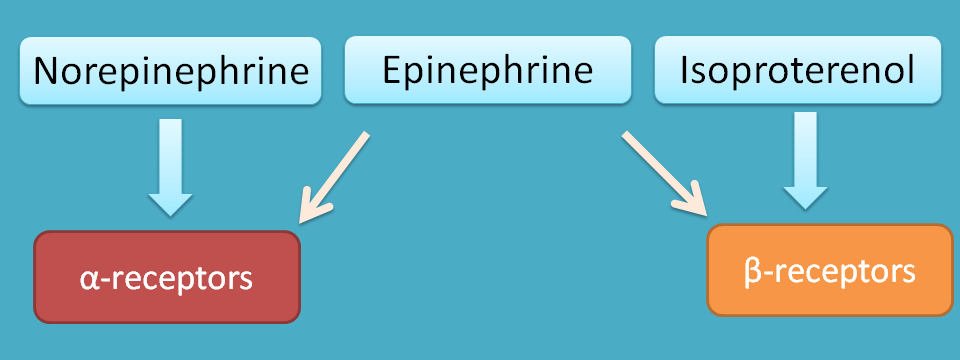
We have already discussed earlier that catechol amines act on adrenergic receptors with different affinities. For example, norepinephrine preferentially acts on alpha receptors while isoprenaline acts on beta receptors. Epinephrine acts both on alpha and beta receptors.
On the other hand dopamine additionally acts on dopamine receptors along with its action on α and β adrenergic receptors.
Non-catechol amines
These drugs don’t have catechol group in their structure but still binds to adrenergic receptors. They can act specifically on any of the adrenergic receptors and hence classified as
- α agonists
- β agonists
α agonists are further classified as
- α1 agonists
- Phenylephrine
- Oxymetazoline
- Xylometazoline
- α2 agonists
- Clonidine
- Apraclonidine
Similarly β agonists are classified as
- β1 agonists
- Dobutamine
- β2 agonists
- Salbutamol
- Terbutaline
- Salmeterol
- Formoterol
Indirectly acting
These drugs increase adrenergic transmission indirectly by
- Displacing norepinephrine from storage vesicles
- Amphetamine
- Tyramine
- Inhibiting uptake
- Tricyclic antidepressants
- Cocaine
- Inhibition of metabolism
- MAO inhibitors
Drugs like TCAs and MAO inhibitors are not specific for adrenergic neurons but also act on serotoninergic and dopaminergic neurons. They mainly act on CNS with peripheral actions as side effects.