Mixed acting adrenergic agonists
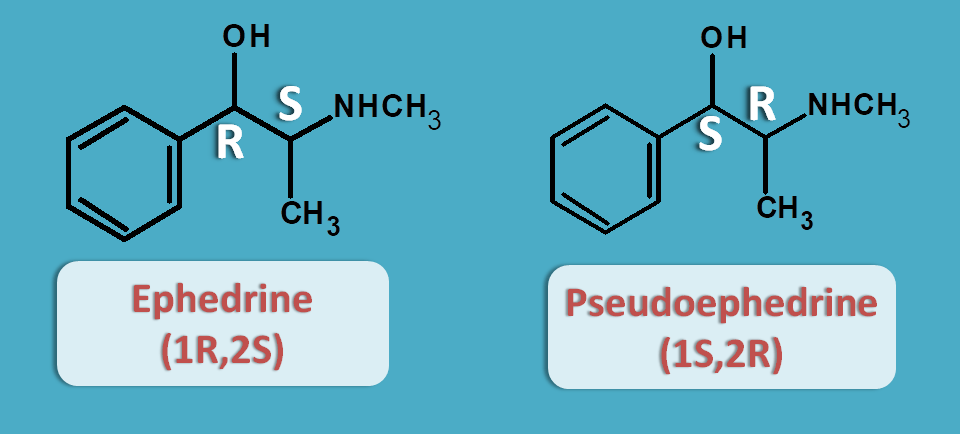
Ephedrine and pseudoephedrine belong to this category. Ephedrine is a natural alkaloid obtained from ephedra species like ephedra sinica and ephedra officialis. Ephedrine and pseudoephedrine differ only in stereochemistry.
How they act?
They act on both alpha and beta adrenergic receptors producing both direct and indirect actions. These drugs can directly bind to the adrenergic receptors and produce cellular effect just like epinephrine. Again these drugs can’t be metabolised by COMT hence bind for longer period.
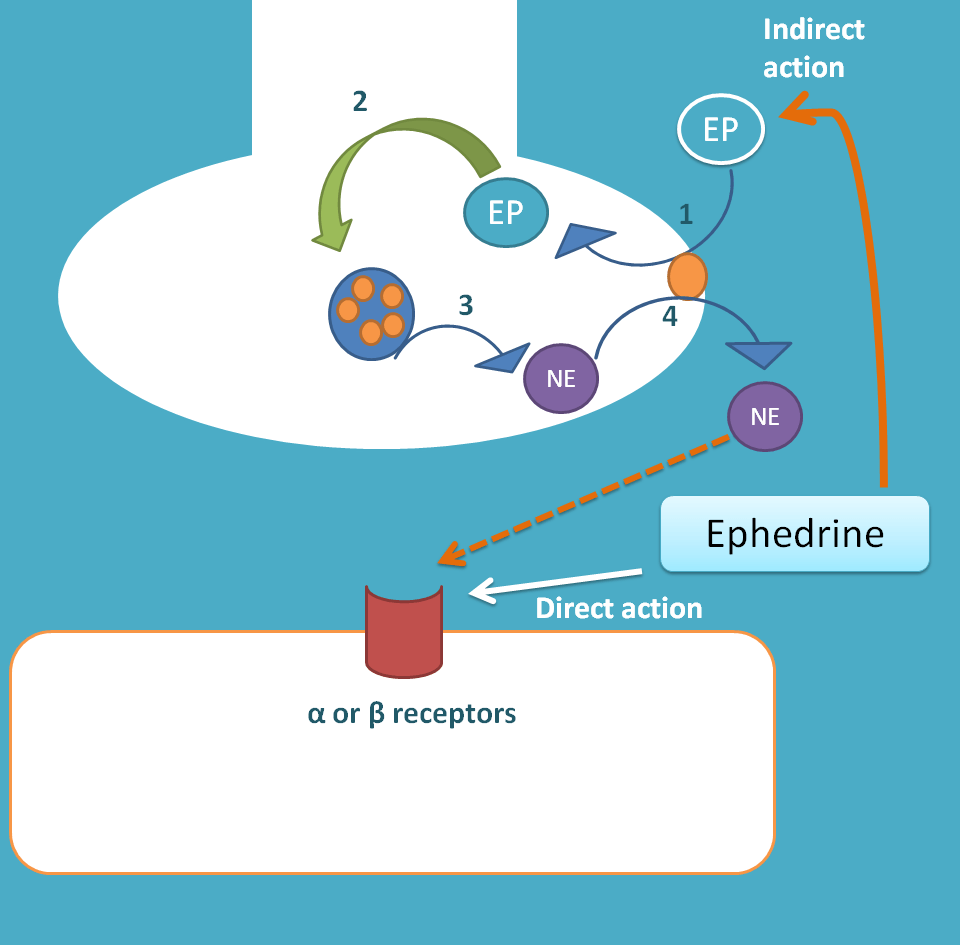
They also show indirect action by entering into the presynaptic nerve terminals by uptake 1 process. Within the nerve terminal they displace the norepinephrine from storage vesicles increasing its leak into synaptic cleft. Increased norepinephrine levels then act on postsynaptic receptors and produce cellular effects.
Pharmacological actions
Pharmacological actions are similar to epinephrine as they act on both of the adrenergic receptors. Various actions mediated by alpha receptors are
- Vasoconstriction leading to rise in blood pressure
- Nasal decongestion
Similarly action on beta receptors produce
- Increase in rate and force of contraction of heart
- Increase in cardiac output
- Bronchodilatation
- Increased renin release
- Increase in blood glucose levels
Apart from these, ephedrine can enter into the CNS and produce euphoria. This can result in drug addiction leading to its abuse. That's why ephedrine use is somewhat limited to nasal decongestion.
Side effects
No need to say that they produce side effects attributed to sympathetic activation.
- Rise in blood pressure
- Tachycardia
- Palpitations
- Anxiety
- Tremor
- Headache
- Tension
- Insomnia
- Euphoria
- Addiction
Indications
Currently ephedrine is very little used while pseudoephedrine is used as nasal decongestant in few of cough syrups.