Actions and uses
Actions
Succinylcholine is a short acting agent that shows duration of action around 10-20 minutes. Even it is stable against acetylcholinesterase, it is metabolised by plasma cholinesterases hence short acting.
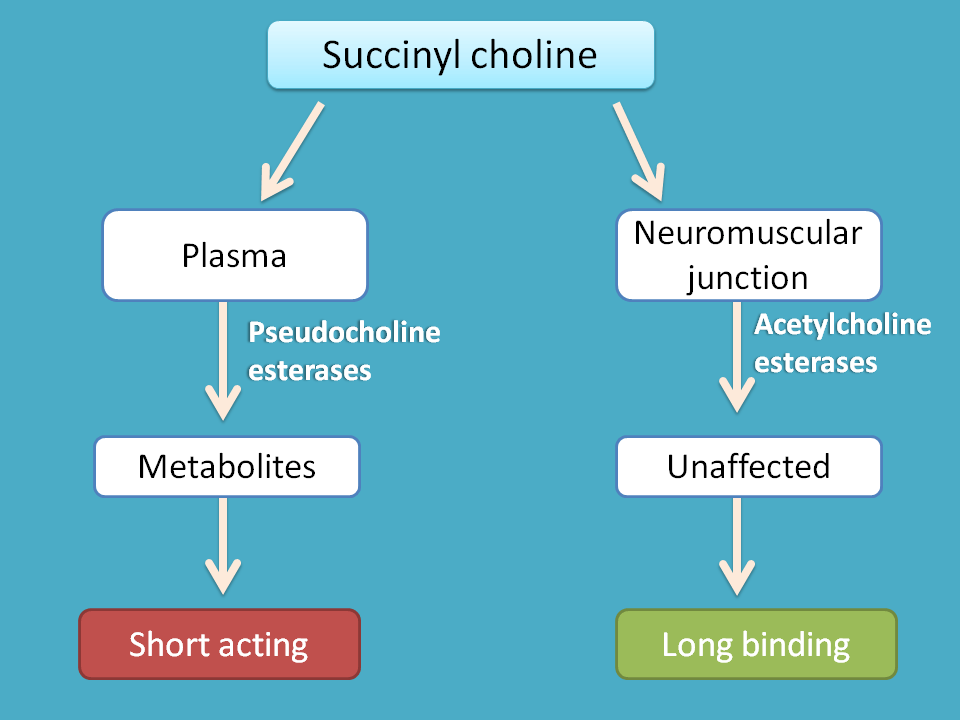
It produces relaxation of skeletal muscle with smaller muscles effected at first. It also shows few muscarinic actions of which the following are significant.
- Bradycardia
- Increase in intraocular tension
Side effects
- Bradycardia
- Postoperative pain
- Hyperkalemia
- Malignant hyperthermia
- Cardiac dysrrhythmias
- Increase in intraocular pressure
Bradycardia
Succinylcholine is not completely selective for nicotinic receptors and shows a minor action at muscarinic receptors. It acts on M2 receptors located on heart and due to agonistic action it decreases the heart rate leading to bradycardia.
Postoperative pain
As it produces contraction before muscle is relaxed, it can also produce postoperative pain and fatigue in the patients.
Hyperkalemia
Succinylcholine can increase the potassium release due to enhanced ionic permeability at neuromuscular junction. This results in elevated levels of potassium resulting in hyperkalemia.
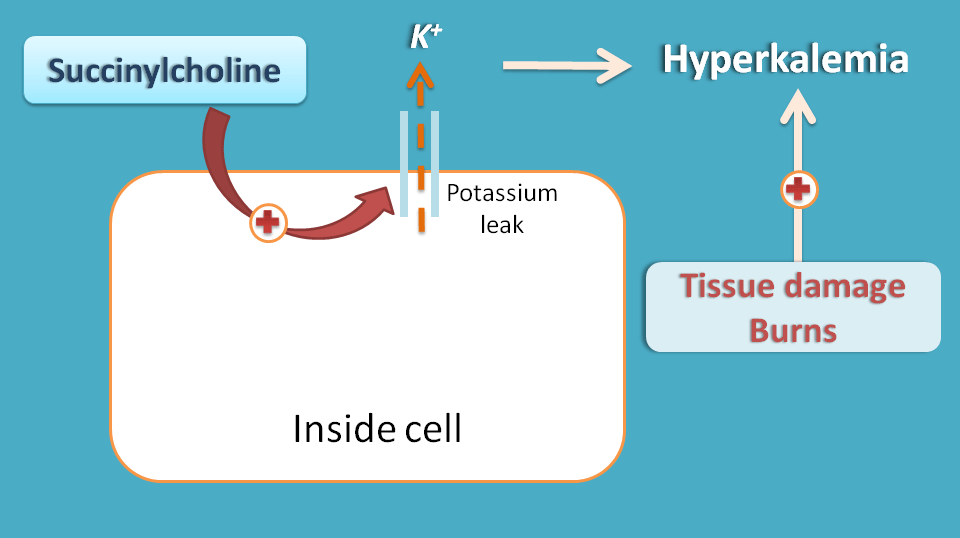
This is further increased in patients with severe tissue damage and burns.
Cardiac dysrrhythmias
Can you expect what happens when potassium levels rise in the body?
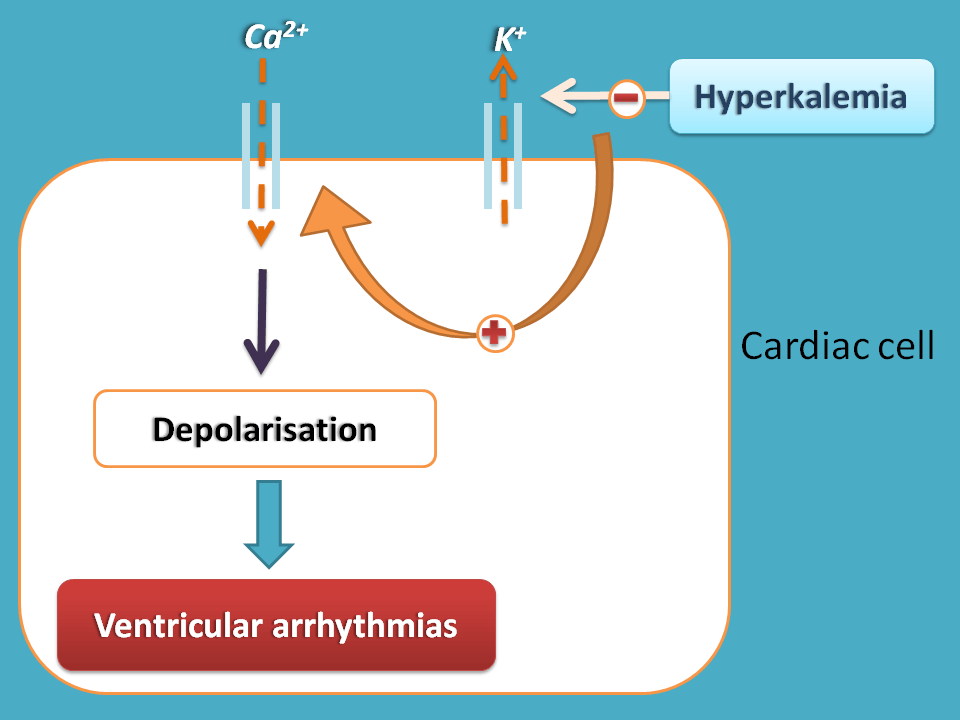
One of the sensitive organs that can be easily affected by electrolyte changes is heart. As the potassium levels are abnormally raised, it can stimulate more calcium entry into cardiac muscle leading to extra depolarisation and ventricular arrhythmias.
Malignant hyperthermia
This is due to excessive muscle contractions produced by this drug initially.
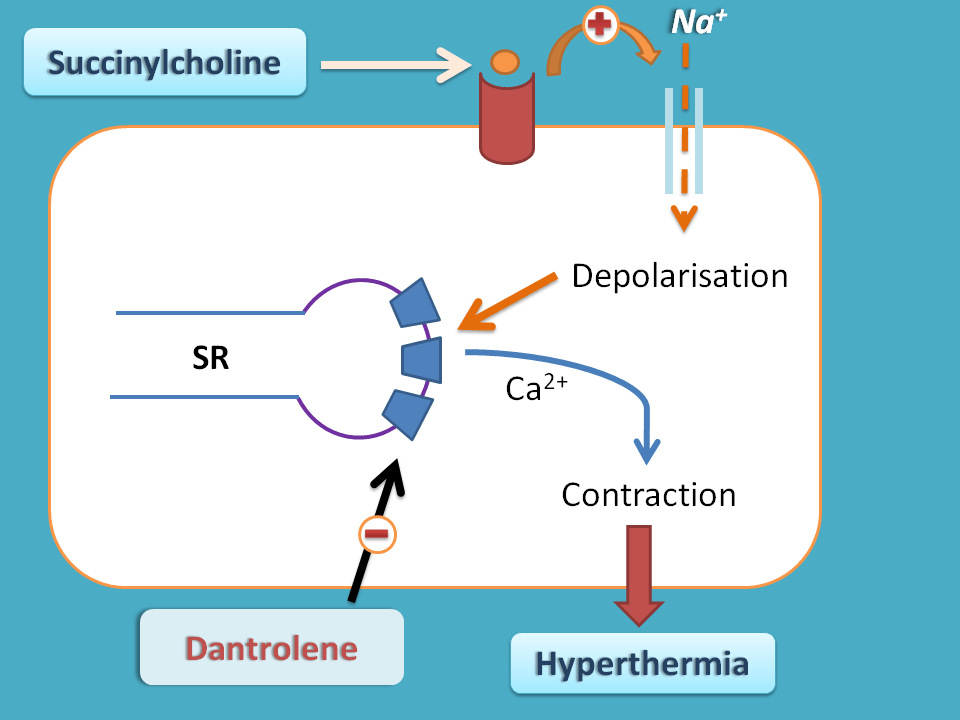
What happens if a machine works continuously? Some heat is generated. Similarly succinylcholine causes continuous muscle contractions which generate heat increasing body temperature. This abnormal rise in temperature is severe hence it is malignant.
Can we treat this malignancy?
Yes, this severe condition can be treated by injection of dantrolene. This drug blocks ryanodine receptors at sarcoplasmic reticulum from which large amount of calcium is released during these contractions.
Increase in intraocular pressure
Succinylcholine can increase intraocular pressure by contraction of muscle involved in the movement of eye.
Where it is used?
Succinylcholine is used for short term muscle relaxation during tracheal intubation where it produces rapid muscle relaxation lasting only for a short period.