Ganglionic blockers
Nowadays, ganglionic blockers are have little importance as they produce mixed effects of both sympathetic and parasympathetic actions.
How they act?
Ganglionic blockers, just like neuromuscular blockers, can act in two ways.
- Depolarising
- Nicotine
- Non-depolarising
- Hexamethonium
- Trimethaphan
Since ganglia is equipped with nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, nicotine acts as depolarising agent and initially stimulates ganglia followed by a block due to persistent depolarisation.
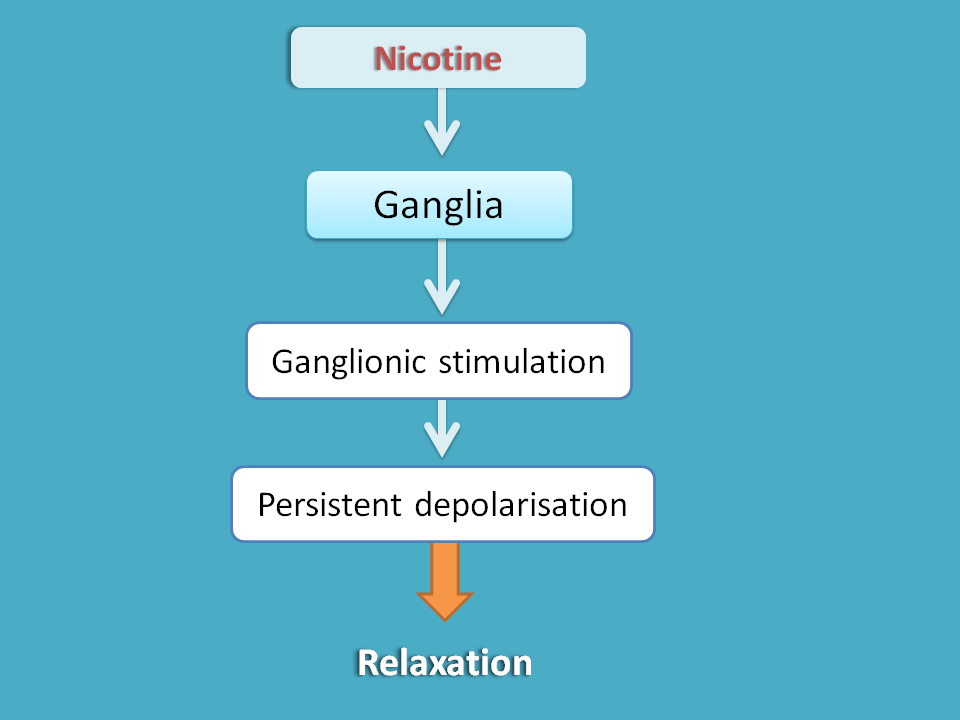
Similarly non-depolarising ganglionic blockers act as antagonists at nicotinic acetylcholine receptors but they are non-selective for sympathetic and parasympathetic ganglia. Therefore they block both parasympathetic and sympathetic ganglia producing mixed effects.
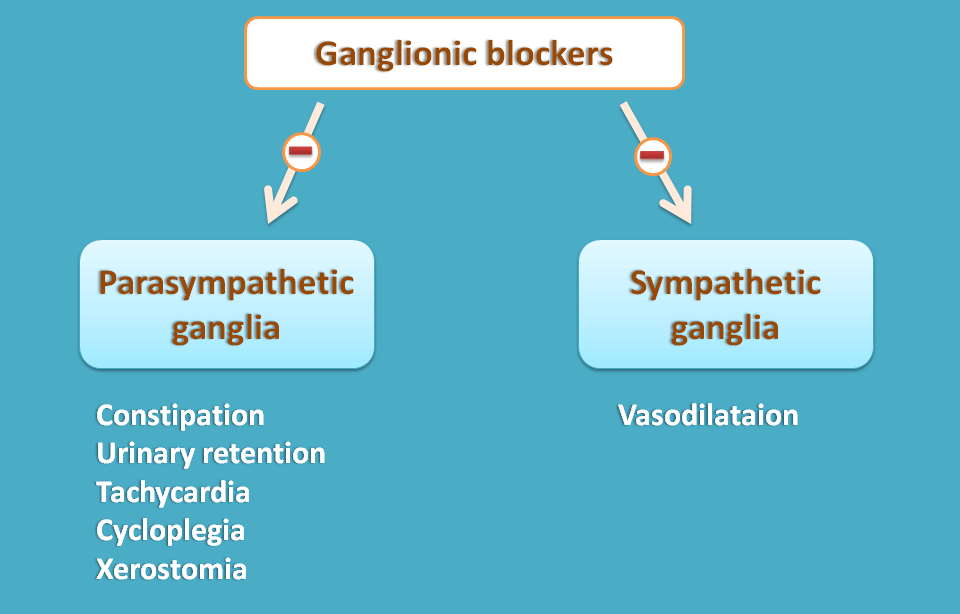
Effects due to block of sympathetic ganglia are
- Vasodilatation
Similarly effects due to block of parasympathetic ganglia are
- Constipation
- Urinary retention
- Tachycardia
- Cycloplegia
- Xerostomia
Indications
Since these drugs produce mixed effect, they have little clinical use and many of these drugs are used as experimental tools.
Due to its vasodilatory effects, trimethapan is used to produce controlled hypotension during surgery to decrease blood loss within the surgical area. It can also be used in pulmonary hypertension and hypertensive emergencies to reduce blood pressure.