- Home >
- Test papers >
MCQ on antihypertensives: Page-4

(A) P and Q
(B) R and S
(C) P,Q and R
(D) P,Q and S
:Adrenaline is vasoconstrictor that is released by sympathetic system that acts predominantly on alpha1 receptors. Acetylcholine acts on M3 receptors present on endothelium and releases nitric oxide. Bradykinin opens potassium channels. Histamine produces all smooth muscle contraction except vascular smooth muscle. It acts through H1 receptors which are coupled with IP3/DAG and thus produce smooth muscle contraction such as bronchoconstriction. At the same time, histamine produces vasodilatation due to release of nitric oxide from endothelium.
(A) Captopril is contraindicated in bilateral renal artery stenosis
(B) ACE inhibitors produce taste disturbances
(C) Thiol group in captopril binds to zinc in ACE
(D) Nitroprusside releases nitric oxide
Not all ACEI produce taste disturbances. Only captopril produces.
(A) Theophylline
(B) Cilostazol
(C) Minoxidil
(D) Dipyridamole
(A) Chlorpromazine
(B) Levodopa
(C) Clozapine
(D) Fenlodapam
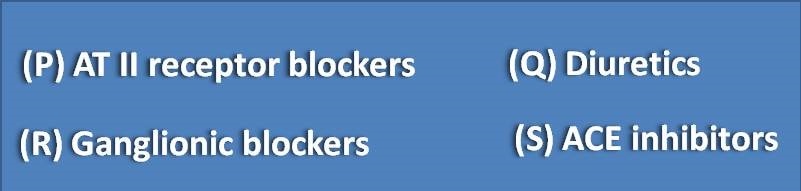
(A) Q
(B) R
(C) P and S
(D) P,Q and R
AT II blockers like sartans are good targets for hypertension. Diuretics also play important role in decreasing body volume and controlling sodium levels in the body and usually combined with other antihypertensives. Phosphodiesterase inhibitors like sildenafil increase cAMP/cGMP levels and produce hypotension at some lower level hence indicated for pulmonary hypertension. Ganglionic blockers block both parasympathetic and sympathetic ganglia and thus produce mixed systemic effects. Even they produce sufficient hypotension because of their unwanted effects like dry mouth, blurred vision they are less tolerated hence not indicated.