Dual innervation
At most of the organs both sympathetic and parasympathetic innervations are present and work either quite oppositely or similarly.
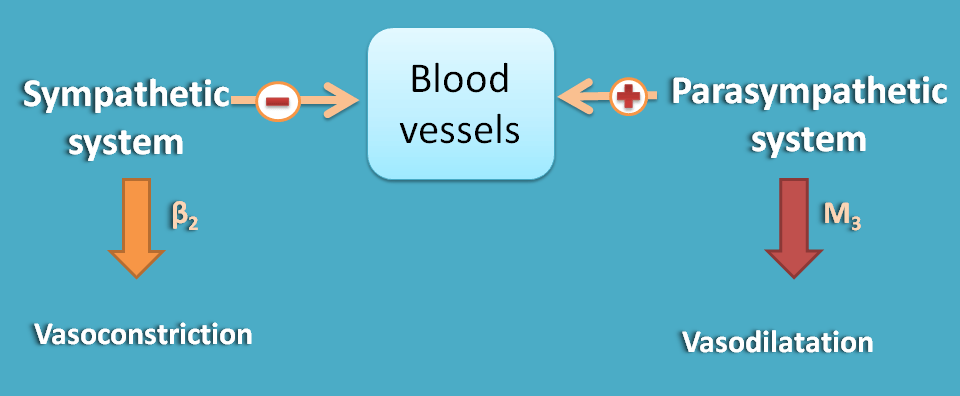
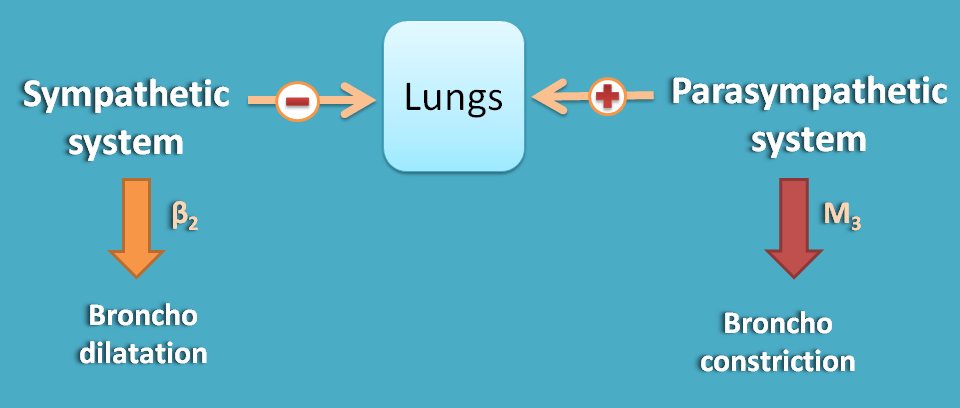
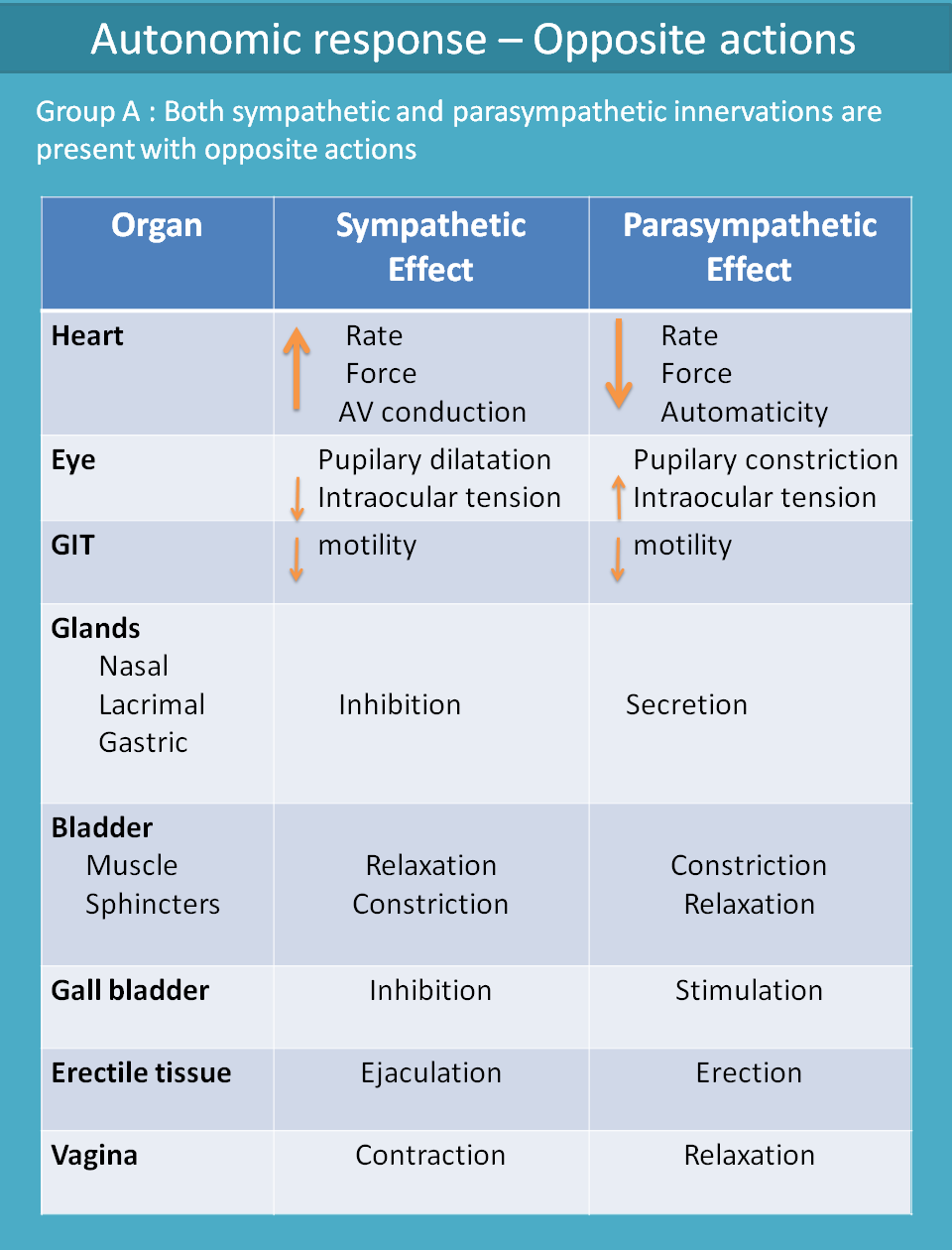
With oppoiste actions
Let's discuss the effect of sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions on each organ along with receptors present. Here we can easily observe that most of the cardiovascular disorders are associated with sympathetic system.
@* *@ @*
*@ @* *@
*@ Heart
As we have discussed in earlier section, the main role of sympathetic system on heart is cardiac stimulation. They increase both force and rate of contraction which finally increases cardiac output. They also increase automaticity, so that non-pacemaker cells can generate their own impulses.
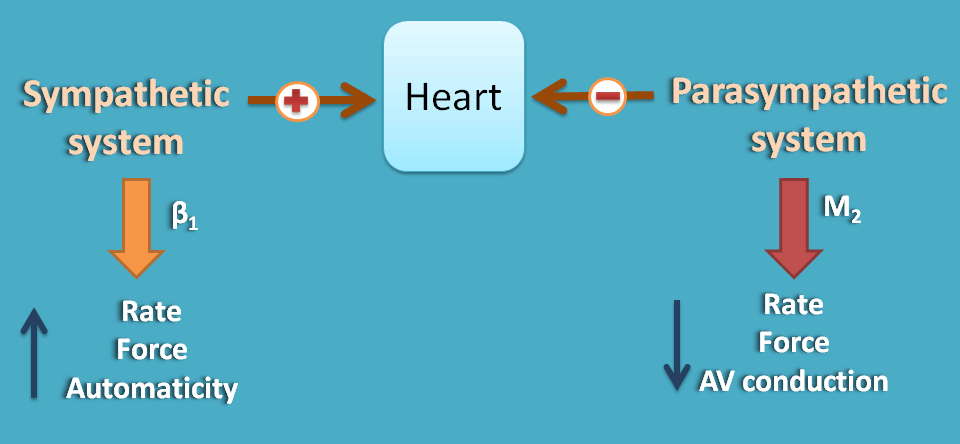
On the otherhand, parasympathetic system decreases both rate and force of contraction hence cardiac output. It also decreases atrioventricular conduction (AV conduction) by its vagal activity.
Eye
Sympathetic system causes contraction of the radial muscle leading to pupilary dilatation. It has no innervation at ciliary muscle hence shows little effect. 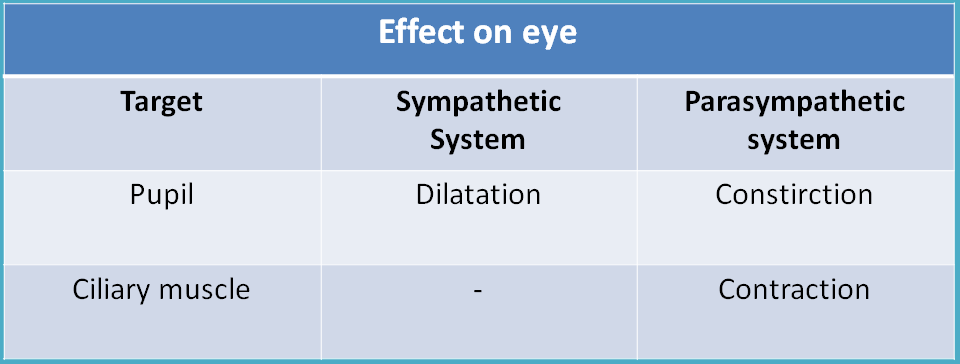
Parasympathetic system produces contraction of circular muscle and ciliary muscle leading to pupilary constriction and adjustment of focal lenght of lens respectively. It also decreases intraocular tension by improving drainage of aqueous humour in anterior chamber of eye.
GI smooth muscle
At GI smooth muscle various receptors like α1, α2 and β2 receptors are present all produce relaxation and decrease in GI motility.
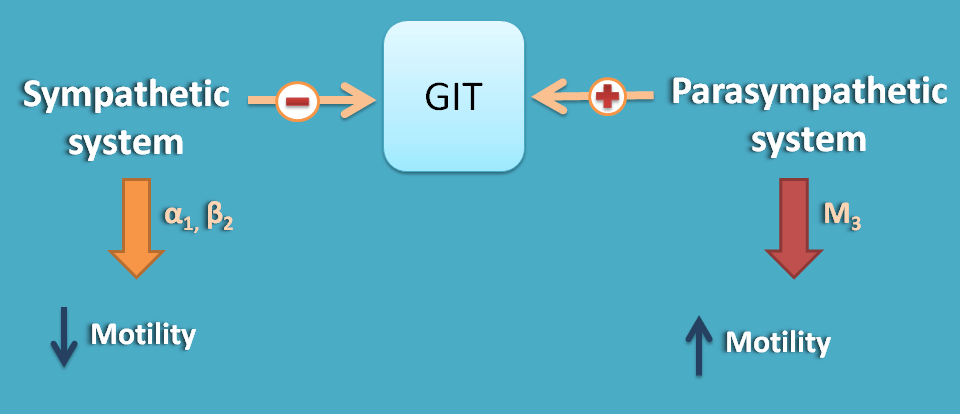
Parasympathetic system increases GI motility by M3 receptors
Bladder
Sympathetic system produces bladder relaxation by β2 receptors whereas parasympathetic system produces bladder constriction through M3 receptors.
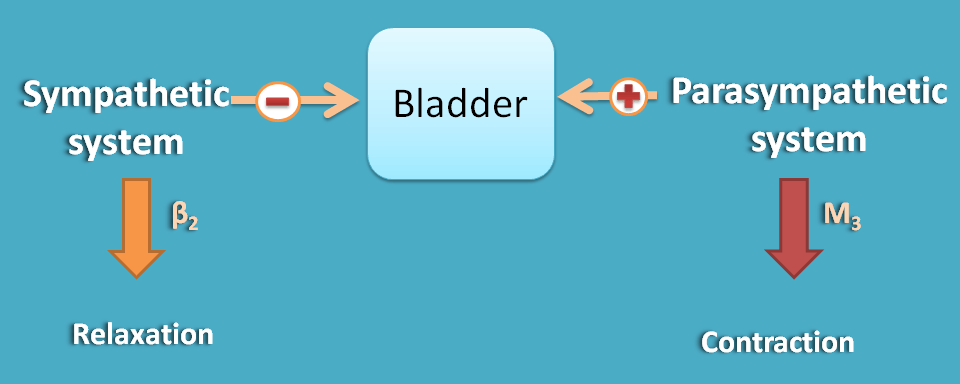
It's quite natural that when bladder constricts, sphincters are simultaneously relaxed to produce micturition. So both sympathetic and parasympathetic systems also affect sphincters accordingly
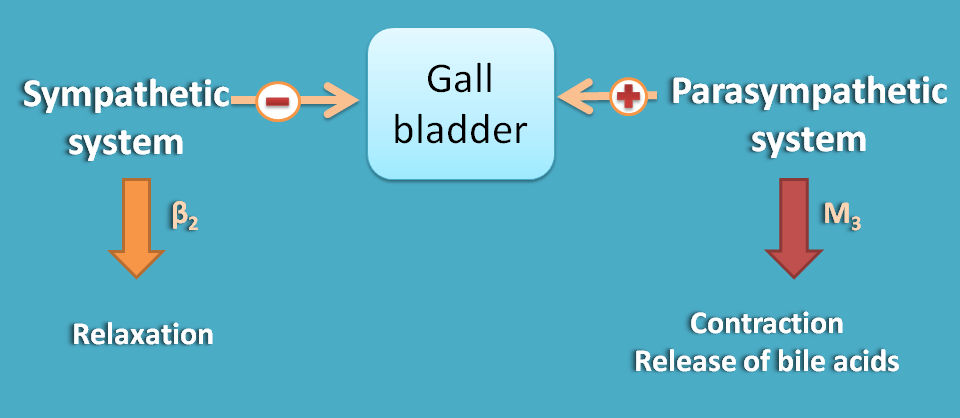
Gall bladder
Gall bladder is relaxed by sympathetic system and contracted to expel bile by parasympathetic system.
Glands
Even sympathetic system has no direct effect on secretion of secretion of nasal, lacrimal and gastric glands it may inhibit their secretion by decreasing the blood supply to these glands.
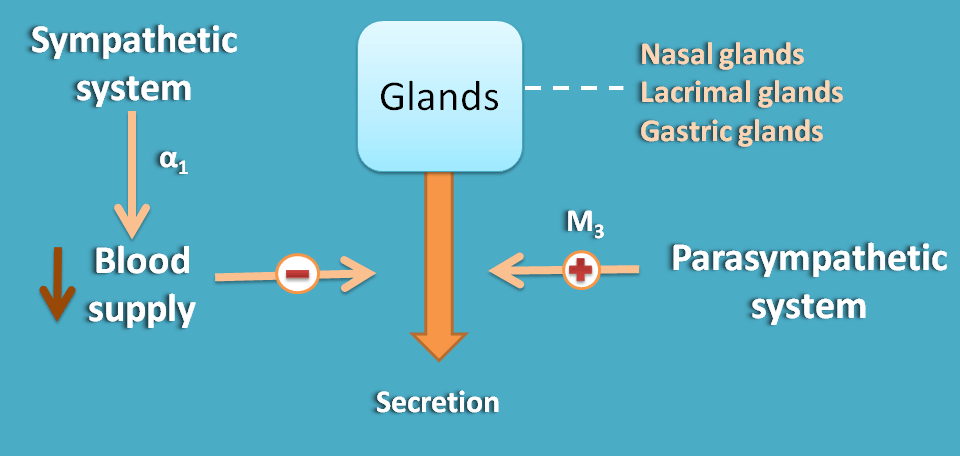
Parasympathetic system stimulates secretion of these glands.
Genitalia
Sympathetic system causes ejaculation of erectile tissue in males and contraction of vagina in females. That's why stress can lead to sexual dysfunction.
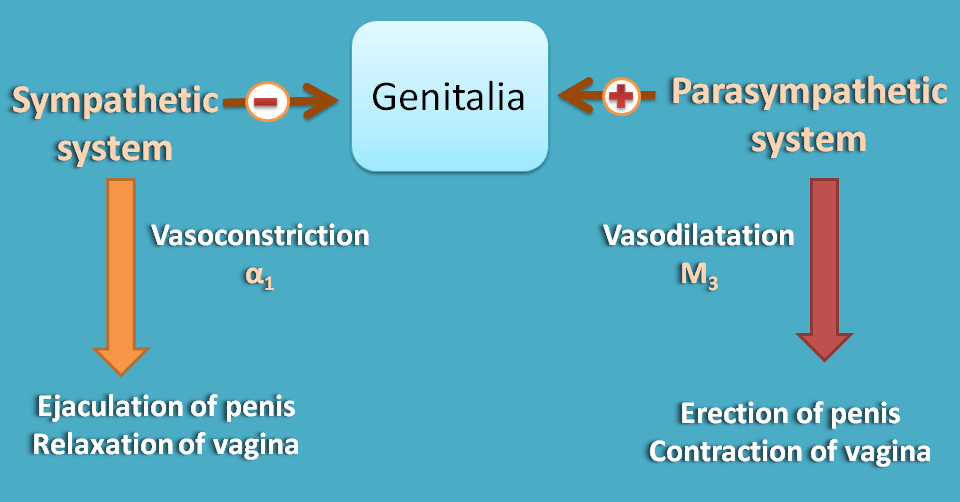
On the other hand, parasympathetic system produces erection of erectile tissue and relaxation of vagina.
All the actions can be summarised below
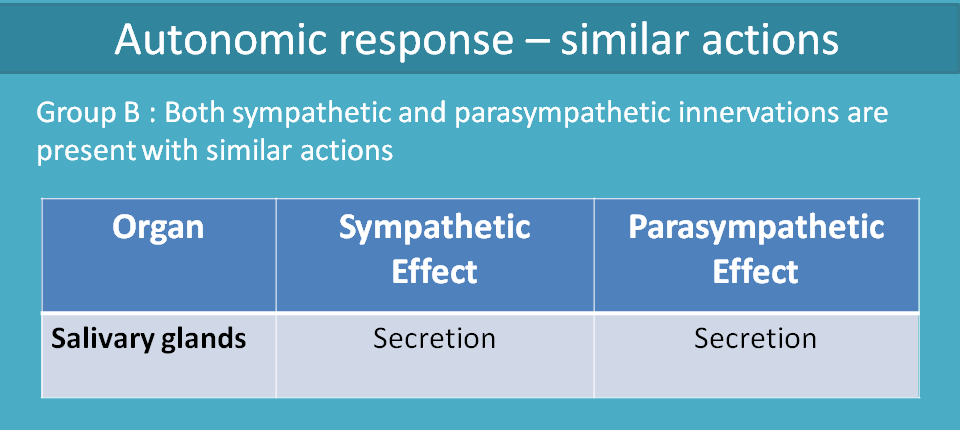
With similar actions
At salivary glands, both sympathetic and parasympathetic systems produce secretion.
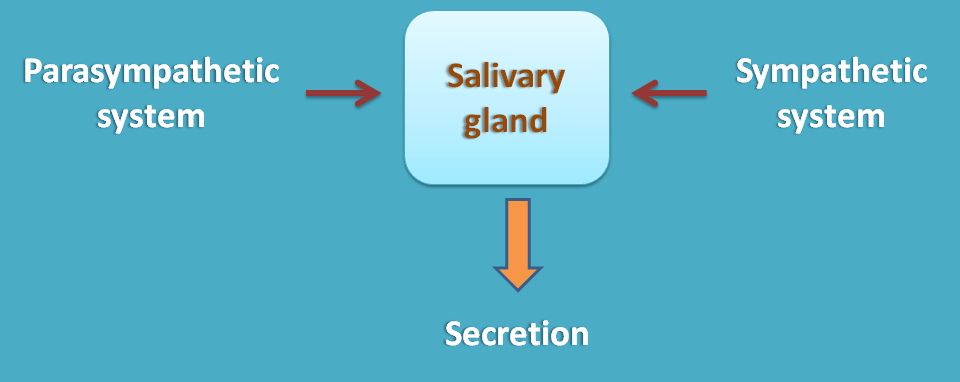
Sympathetic system produces thick viscous saliva whereas parasympathetic system produces profound saliva secretion which is low viscous and watery in nature.