Parasympathetic division
Location of ganglia
The first thing we should note in parasympathetic system is the location of ganglia. The parasympathetic ganglia lie very close to the target organs and in few organs like vagal and pelvic organs it is almost present directly on the target organ.
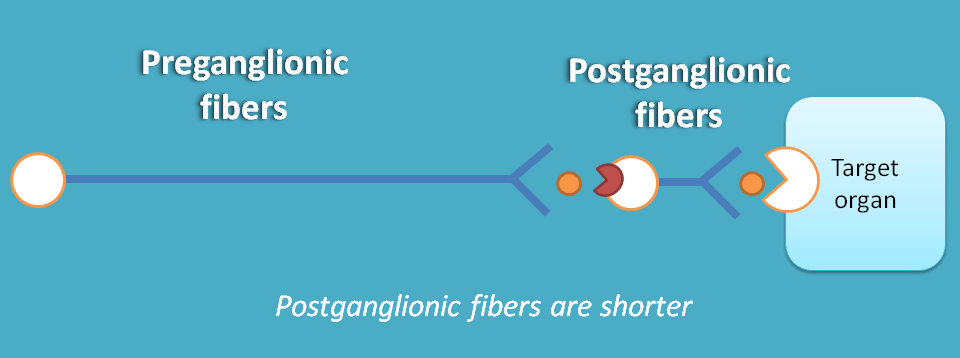
Obviously, the length of pre and post ganglionic fibers differ where preganglionic fibres are longer than post ganglionic fibres.
Outflow
The origin of impulses from CNS that bring parasympathetic discharge are called as parasympathetic outflow. Parasympathetic outflow can be called as cranio-sacral outflow as the fibers emerge along with cranial nerves from brain stem and from sacral region of spinal cord.
Cranial outflow
The cell bodies of the parasympathetic preganglionic fibres lie within the brain stem and emerge along with few of the cranial nerves.
Cranial outflow supplies to the organs above the thoracic region and upper GI regions along with the cranial nerves- III, VII, IX and X.
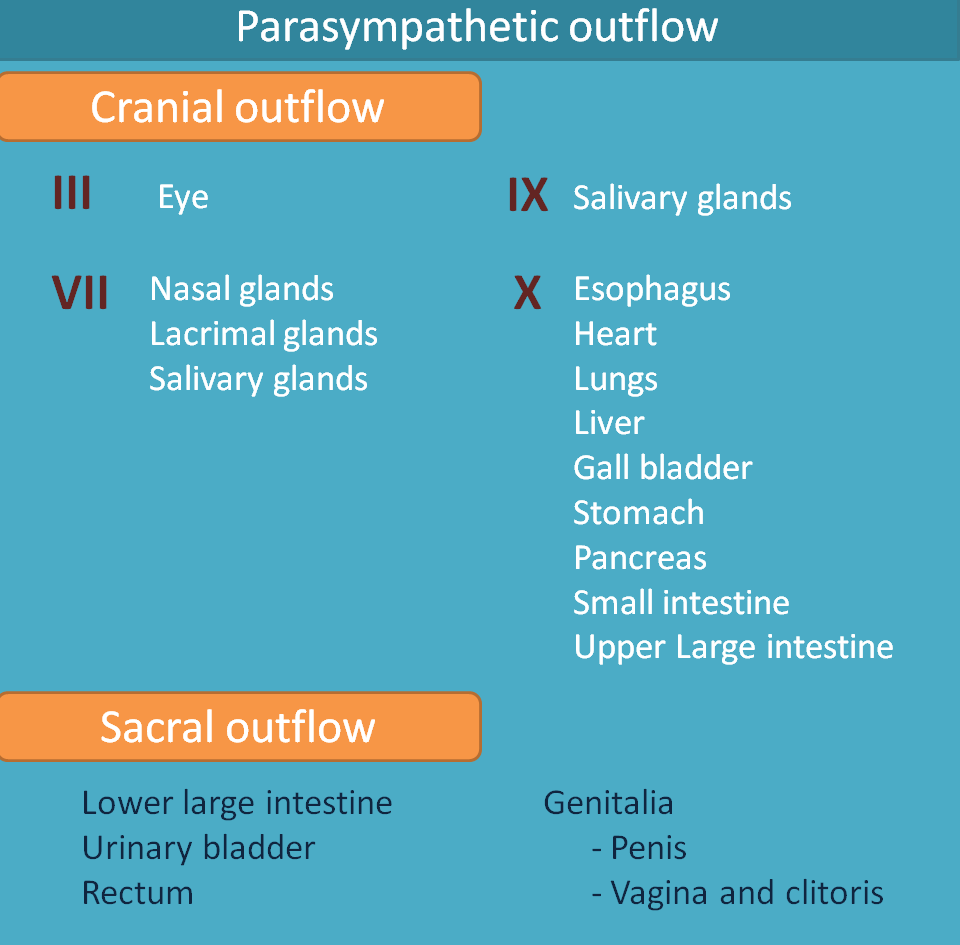
Cranial nerve III - Occulomotor nerve
The parasympathetic fibers from occulomotor nerve supplies to
- Eye
Two important muscle in the eye such as ciliary muscle and circular muscle are supplied by these neurons.
Cranial nerve VII - Facial nerve
The parasympathetic fibers from facial nerve supplies to
- Nasal glands
- Nasopharynx
- Lacrimal glands
- Salivary glands
Cranial nerve IX - Glossopharyngeal nerve
Glossopharyngeal nerve mainly supplies to salivary glands
Cranial nerve X - Vagus nerve
One of the largest nerve that carries many of the parasympathetic fibers to various organs is vagus nerve. This nerve mainly supplies to
- Oesophagus
- Heart
- Lungs
- Liver
- Gall bladder
- Stomach
- Pancreas
- Small intestine
- Upper Large intestine
Sacral outflow
Here the preganglionic fibres emerge from the sacral region of spinal cord supplying the pelvic and abdominal viscera.
Organs supplied by this outflow include
- Lower large intestine
- Urinary bladder
- Rectum
- Genitalia
- Penis
- Vagina and clitoris