Basics of ANS - Introduction
Neurons
Neurons are basic physiological units that form a communication between different organs within the body. They can send the signals at a rapid rate and maintain the physiological functions co-ordinating CNS with periphery.
All neurons are of similar type?
As the function of neurons is diverse, all these can't fit into one shell of definition. Based on their function, neurons can be classified into three types.
- Afferent neurons
- Efferent neurons
- Interneurons
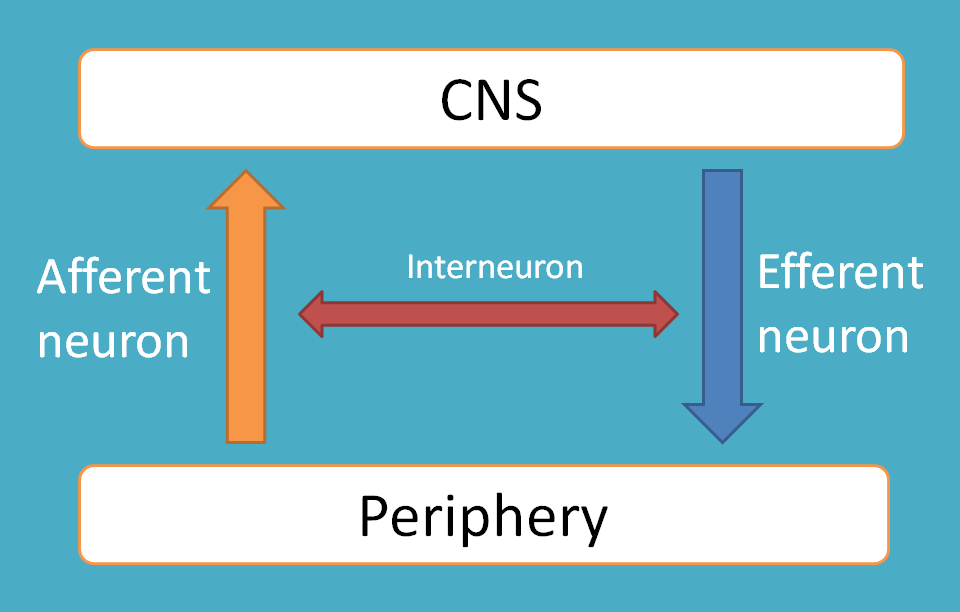
Afferent neurons
Afferent neurons, also known as sensory neurons, are those that conduct impulses from the sensory organs at periphery to the central nervous system. As these neurons sense various stimuli and send the information to the CNS, they are called as sensory neurons. These sensory neurons are equipped with sensory receptors whihc respond to various stimuli.
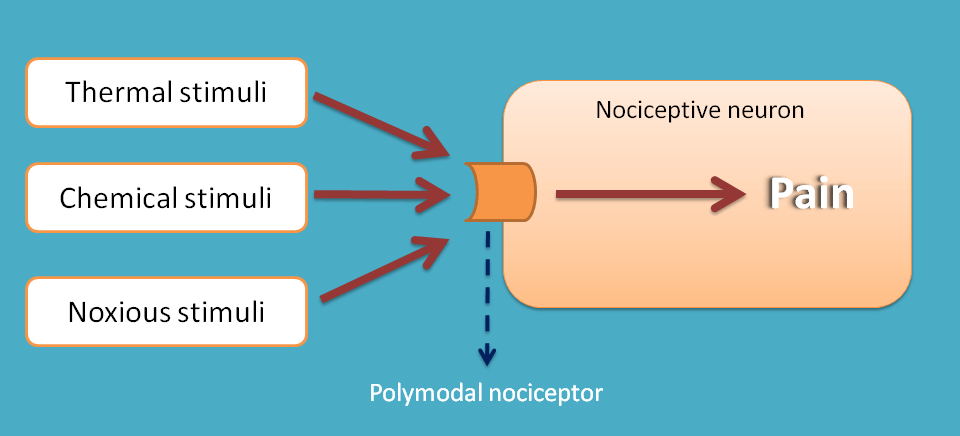
For example, thermoceptors present on the skin can respond to any change in the temperature and send the signal to the brain. Similarly mechanoceptors respond to stretch of smooth muscle like GIT. These sensory receptors are specific to a stimuli hence named accordingly.
- Photoreceptors - Respond to light
- Mechanoreceptors - Respond to mechanical pressure
- Chemoreceptors - Respond to chemicals
- Thermoreceptors - Respond to temperature
- Nociceptors - Respond to pain stimuli
In few neurons like nociceptive neurons, a specialised polymodal nociceptors are present which respond to multiple stimuli.
Efferent neurons
On the other hand, efferent neurons conduct impulses from the central nervous system to the effector organs such as muscle or glands. These are also called as motor neurons as they produce motor actions such as change in the tone of the muscle or secretion of glands.
Inter neurons
Interneurons, also known as connector neurons, are those neurons that connect sensory neurons to motor neurons. These are the neurons that form a bridge between afferent and efferent neuron that share some information between the two major pathways.