Functional role of ANS
Now let’s discuss the functions of both parasympathetic and sympathetic systems. It is well familiar that these two systems act quite oppositely and maintain the homeostasis in the body. But it is not completely true.
Sympathetic and parasympathetic systems work quite oppositely at many of the organs but not at all organs.
❞There are many organs where only one system is acting or both the systems producing similar actions.
For example, at salivary glands both produce same effect i.e. secretion.
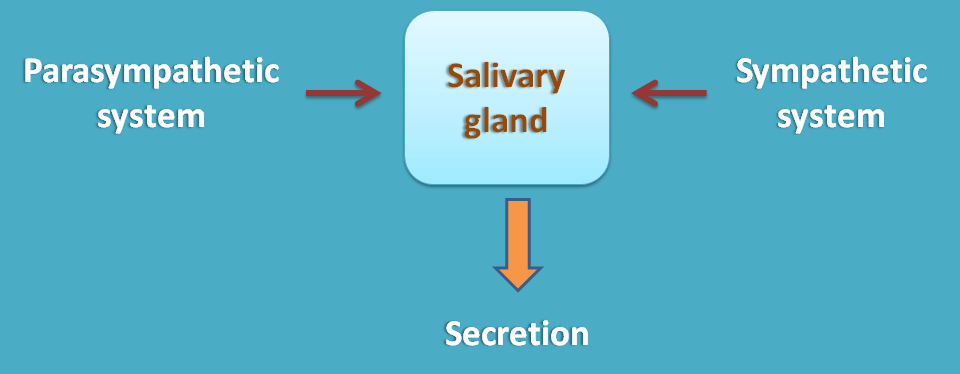
Even they have few exceptions, it is better to start our discussion by keeping two important facts in our mind.
- Both systems work oppositely at many organs.
- Sympathetic system is activated under stressful conditions
Let’s illustrate our discussion with simple example.
Suppose you are attempting a competitive exam. No doubt you will be in under the stress. Exam was initiated and you are about to attempt first question. Let’s see what happens to different organs in your body.
Heart
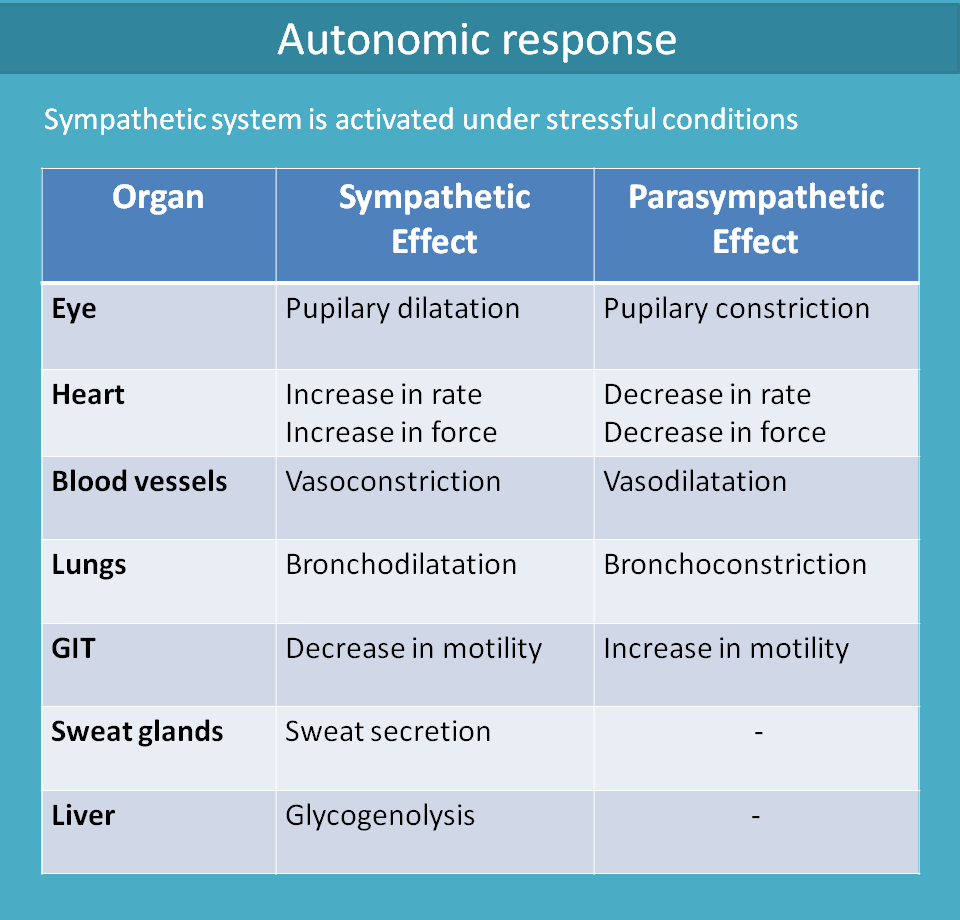
You are getting little tension and your heart beat increases. You can feel a rise in your heart beat. This is essential as vital organs like brain require more blood supply so your heart beats at higher rate and force to increase the cardiac output. Parasympathetic system produces quite opposite effect on the heart.
| Organ | Sympathetic effect | Parasympathetic effect |
|---|---|---|
| Heart | ↑ Rate ↑ Force | ↓ Rate ↓ Force |
Liver
Next, you require more energy so more glucose in the blood. Hence your liver tries to produce more glucose by increasing glycogenolysis i.e. breakdown of glycogen to glucose.
| Organ | Sympathetic effect | Parasympathetic effect |
|---|---|---|
| Liver | ↑ Glycogenolysis | - |
Here parasympathetic system has no effect.
Eyes
Fine, you have more blood supply and sufficient glucose in your blood. Now you are going to attempt first question.
First question doesn’t appear clear. (It will be more blurred if you don’t know the answer !!)
So your puplils will dilate to see the question clearly.
| Organ | Sympathetic effect | Parasympathetic effect |
|---|---|---|
| Eye | Pupilary dilatation | Pupilary constriction |
Here again parasympathetic system produces opposite effect.
Lungs
Now you have read the question and you are thinking for a right answer. You will take a long breath and your bronchioles are more dilated to increase the oxygen supply to the brain cells.
| Organ | Sympathetic effect | Parasympathetic effect |
|---|---|---|
| Lungs | Bronchodilatation | Bronchoconstriction |
Blood vessels
Your systemic blood vessels constrict and blood pressure slowly rises to withstand this stressful condition. At the same time few of the blood vessels supplying to skeletal muscle are dilated to supply more energy to skeletal muscle. Otherwise you can’t hold a pen, stand or run under any stressful conditions.
| Organ | Sympathetic effect | Parasympathetic effect |
|---|---|---|
| Blood vessels | Vasoconstriction Vasodilatation (at skeletal muscle) | Vasodilatation |
GI smooth muscle
As more blood is required to your brain, most of the blood is diverted and your GIT gets less blood supply and finally motility is decreased to save energy.
| Organ | Sympathetic effect | Parasympathetic effect |
|---|---|---|
| GI smooth muscle | ↓ motility | ↑ motility |
Sweat glands
As you are under stress and your brain is working at high rate, a lot of heat is generated which is dissipated by sweat secretion.
| Organ | Sympathetic effect | Parasympathetic effect |
|---|---|---|
| Sweat glands | Secretion | - |
Again here, parasympathetic system has no effect.
All the above actions can be summarised below.
Eventhough the above explanation describes the physiological control of sympathetic and parasympathetic system, it is an oversimplification and the original situation is very complex and includes many exceptions which are described below.
At few of the organs, both sympathetic and parasympathetic innervations are present (dual innervation) whereas at other organs only single innervation is present.
To discuss in-depth, let’s divide the function of sympathetic and parasympathetic systems into following categories.
- Dual innervation
- With opposite actions
- With similar actions
- Single innervation
- Only sympathetic innervation
- Only parasympathetic innervation
We will discuss these in detail in the next section.